如右图所示,有人制作了一个家庭制氧装置。该制氧装置由2个可乐瓶、2根软管连接而成。制氧时,先在甲瓶中加入20 g的水,再往甲瓶中加入157 g过氧碳酸钠(化学式为2Na2CO3·3H2O2,相对分子质量为314)和少量二氧化锰,产生的气体通过软管从乙瓶导出,即可供人吸氧。在甲瓶中发生的化学反应方程式为:
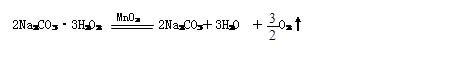

(1)这包总质量为157 g的过氧碳酸钠完全反应,理论上可
生成多少克氧气? 多少克H2O?
(2)完全反应后,甲瓶溶液中溶质的质量分数。(计算结果精确到0.1%)
(1)24g氧气,27gH2O (2)69.3%
题目分析:(1)依据过氧碳酸钠分解的反应方程式,利用过氧碳酸钠与氧气、水的质量比,由过氧碳酸钠的质量可求出生成氧气和水的质量。
(2)再依据反应方程式中过氧碳酸钠与碳酸钠的质量比,可求出生成的碳酸钠的质量;最后依据质量守恒定律,可求出反应剩余的溶液的总质量,即可求出反应后溶质的质量分数。
解:设这包总质量为157 g的过氧碳酸钠完全反应,理论上可生成氧气和H2O的质量分别是x、y,Na2CO3的质量为z。
2Na2CO3·3H2O2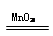 2Na2CO3+3H2O+
2Na2CO3+3H2O+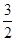 O2↑
O2↑
314 212 54 48
157g z y x
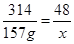 ,解得x=24g
,解得x=24g
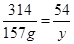 ,解得y=27g
,解得y=27g
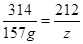 ,解得z=106g
,解得z=106g
(2)依据质量守恒定律可知,完全反应后溶液的质量=157g+20g–24g=153g
所以,完全反应后,甲瓶中Na2CO3的质量分数=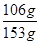 ×100%=69.3%
×100%=69.3%
答:理论上可生成24g氧气,27gH2O,完全反应后,甲瓶溶液中溶质质量分数为69.3%。
点评:此题是关于化学方程式及溶质质量分数的计算题,要求学生要有较强的分析能力;本题难度不大,能根据相关的化学反应方程式,并依据已知量对未知的应求量进行求解计算即可,注意解题要规范。
