问题
多选题
| 如图所示,质量相同的木块A、B用轻弹簧连接置于光滑的水平面上,开始弹簧处于自然状态,现用水平恒力F推木块A,则从开始到弹簧第一次被压缩到最短的过程中,以下说法正确的是( ) A.两木块速度相同时,加速度aA=aB B.两木块速度相同时,加速度aA<aB C.两木块加速度相同时,速度vA<vB D.两木块加速度相同时,速度vA>vB 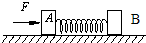 |
答案
BD
| 如图所示,质量相同的木块A、B用轻弹簧连接置于光滑的水平面上,开始弹簧处于自然状态,现用水平恒力F推木块A,则从开始到弹簧第一次被压缩到最短的过程中,以下说法正确的是( ) A.两木块速度相同时,加速度aA=aB B.两木块速度相同时,加速度aA<aB C.两木块加速度相同时,速度vA<vB D.两木块加速度相同时,速度vA>vB  |
BD