问题
选择题
关于下图的叙述,正确的是( )
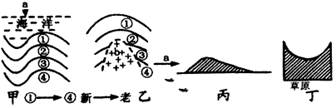
A.甲图表示的地层中,②地层含有石油,开采时应在a处钻井
B.乙图表示的地层中,b处绝对不会含有化石
C.丙图表示流动沙丘,其所在地的盛行风向如a箭头所示
D.丁图所示地形是流水侵蚀作用形成的
答案
答案:B
背斜是良好的储油构造,开采时应该在背斜顶部,故A错。化石存在于沉积岩中,岩浆岩中不可能有化石的存在。不管是静止沙丘还是移动沙丘,其迎风坡一侧较为和缓。丁图所示地形为‘U’形谷,应该为冰川侵蚀地貌。
