某化学小组采用下图装置模拟电解饱和食盐水制备氢气,通过氢气还原氧化铜测定Cu的相对原子质量,同时检验氯气的氧化性(图中夹持和加热仪器已经略去).
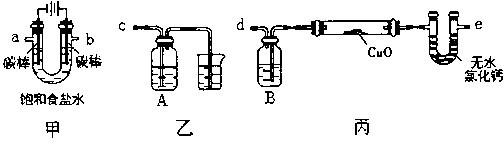
(1)写出装置甲中反应的离子方程式______.为完成上述实验,正确的连按方式为a连接______,b连接______(填字母).
(2)①装置乙烧杯中液体的作用是______.A瓶内盛装的溶液最好是______(填字母).
a.I2-淀粉溶液b.NaOH溶液 c.FeCl2与KSCN混合溶液d.Na2SO3溶液
②加热装置丙中的氧化铜粉末之前,除了要检查该装置的气密性还需进行的必要操作是______.
(3)利用装置丙测定Cu的相对原子质量,现有两种方案:①测得反应前后洗气瓶B及其中液体质量差m1,②测得反应前后U形管及其中固体质量差m2.你认为合理的方案为______(填“①”或“②”).若采用测得反应后硬质玻璃管中剩余固体的质量m3的方案,已知O的相对原子质量为16,实验中氧化铜样品质量为m,则测定Cu的相对原子质量的表达式为______,该方案在反应后硬质玻璃管冷却过程中没有一直通氢气,会导致测定Cu韵相对原子质量______(填“偏大”、“偏小”或“无影响”),理由是______.
(1)电解饱和食盐水时,阳极上氯离子放电生成氯气,阴极上氢离子放电生成氢气,溶液中同时生成氢氧根离子,所以电解反应离子方程式为2Cl-+2H2O
2OH-+H2↑+Cl2↑,要检验氯气的氧化性,则氯气连接强还原性的物质且反应现象要明显,故选c,用氢气还原氧化铜来检验氢气,因为电解得到的氢气中含有水蒸气,所以在实验前要除去水蒸气,故选e,电解 .
故答案为:2Cl-+2H2O
2OH-+H2↑+Cl2↑;e;c;电解 .
(2)①氯气有毒,不能直接排空,氯气和水反应生成酸,所以氯气可以用碱性物质来处理,所以装置乙烧杯中液体的作用是吸收多余的氯气,防止环境污染;
氯气具有强氧化性,能氧化强还原性的物质,要检验氯气,必须选用强还原性的物质且反应现象明显,
a.氯气能氧化碘而使溶液褪色,氯气和水反应生成的次氯酸也能使溶液褪色,所以无法证明氯气的氧化性,故不选;
b.氯气和氢氧化钠溶液反应生成氯化钠和次氯酸钠,反应现象不明显,故不选;
c.氯气能把亚铁离子氧化成三价铁离子,铁离子和硫氰化钾溶液反应生成血红色溶液,反应现象明显,且能检验氯气的氧化性,故选;
d.氯气能氧化亚硫酸钠生成硫酸钠,但反应前后溶液颜色不变,反应现象不明显,故不选;
故答案为:吸收多余的氯气,防止环境污染;c;
②氢气是可燃性气体,与氧气混合,加热容易发生爆炸危险,加热氧化铜之前要通入氢气排尽装置内空气,故答案为:通入氢气排尽装置内空气;
(3)①中质量的差量是氢气还原氧化铜得到的物质,与铜有关,所以能计算铜的相对原子质量,②中质量的差量是氢气中原来的水蒸气,与铜无关,所以不能计算铜的相对原子质量,故选①;
硬质玻璃管中的质量差是氧元素的质量=m-m3,
设铜的相对原子质量为x,
CuO------O
1 16
m-m3m x+16
x=
,16m3 m-m3
反应生成的铜被空气的氧气氧化使m3数据增大,则
偏大,所以导致测定结果偏大,16m3 m-m3
故答案为:①;
;偏大;反应生成的铜被空气的氧气氧化使m3数据增大,导致测定结果偏大.16m3 m-m3
