如图是模拟电化学反应装置图.下列说法正确的是( )
A.开关K置于N处,则铁电极的电极反应式为:Fe-2e→Fe2+
B.开关K置于N处,可以减缓铁的腐蚀
C.开关K置于M处,则铁电极的电极反应式为:2Cl--2e→Cl2↑
D.开关K置于M处,电子从碳棒经开关K流向铁棒
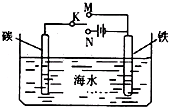
A.开关K置于N处,该装置是电解池,铁电极是阴极,阴极上得电子发生还原反应,故A错误;
B.开关K置于N处,该装置是电解池,碳棒作阳极,阳极上溶液中阴离子失电子发生氧化反应,铁棒作阴极,铁棒上阳离子得电子发生还原反应,所以可以减缓铁的腐蚀,故B正确;
C.开关K置于M处,该装置是原电池,铁作负极,铁电极的电极反应式为:Fe-2e-→Fe2+,故C错误;
D.开关K置于M处,该装置是原电池,碳棒作正极,铁棒作负极,电子从铁棒沿导线流向碳棒,故D错误;
故选B.
