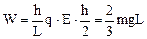如图所示,MN、PQ为水平放置、相距为d的两平行金属板,两板间电压为U,且上板带正电,板MN中央有一个小孔O,板间电场可认为匀强电场。AB是一根长为L(L<d)、质量为m的均匀带负电的绝缘细杆。现将杆下端置于O处,然后将杆由静止释放,杆运动过程中始终保持竖直。当杆下落L/3时速度达到最大。重力加速度为g。求:
(1)细杆带电荷量;
(2)杆下落的最大速度;
(3)在杆下落过程中,杆克服电场力做功的最大值。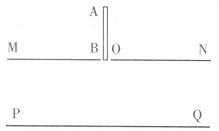
(1)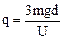 (2)
(2)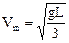 (3)
(3)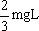
(1)设杆的带电量为q,板间电场强度为E。杆下落L/3时,a=0,则

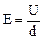 两式解得
两式解得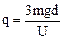
(2)杆下落L/3时,速度最大,由动能定理得
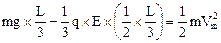 联立②、④式解得
联立②、④式解得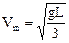
(3)当杆下落速度为零时,杆克服电场力做功最大,设此时杆下落距离为h,则
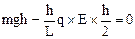
解得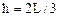 杆克服电场力做功
杆克服电场力做功