如图,真空中有两个带等量异种点电荷A、B,C、D、O是AB连线的垂线上的点,且有AO>BO,A带负电B带正电。一带负电的试探电荷从C运动到D,下列说法正确的是
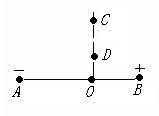
A.C、D两点的电势相等
B.试探电荷在C点的受到的电场力要大些
C.试探电荷在C点的电势能大于在D点的电势能
D.在此电场中具有-15J电势能的带电粒子比具有-5J电势能的带电粒子的电势能大
答案:C
题目分析:根据等量异种点电荷的电场线、等势面分布可知C点电势低于D点电势,A错误,
C点的电场线比D点的电场线较疏,所以D点场强较大,C点的电场强度较小,所以试探电荷在C点的电场力小一些,B错误,
过程中电场力做正功,电势能减小,所以C点的电势能大于D点的电势能,C正确,
根据电势能定义可得D错误,
点评:电场线是从正电荷或者无穷远出发出,到负电荷或无穷远处为止,沿电场线的方向,电势降低,电场线密的地方电场的强度大,电场线疏的地方电场的强度小,电场力做正功,电势能减小,电场力做负功,电势能增加.

