已知△ABC∽△DEF,AB=6cm,DE="12cm," 且△ABC的周长为24cm,则△DEF的周长为 。
48 cm
题目分析:已知△ABC∽△DEF,所以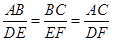 ,因为AB=6cm,DE=12cm,所以
,因为AB=6cm,DE=12cm,所以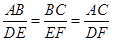 =
=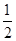 ,又因为△ABC的周长为24cm,即AB+BC+CA=24;则△DEF的周长=DE+EF+DF=2(AB+BC+CA)=48
,又因为△ABC的周长为24cm,即AB+BC+CA=24;则△DEF的周长=DE+EF+DF=2(AB+BC+CA)=48
点评:本题考查相似三角形,解答本题的关键是掌握相似三角形的性质,运用其性质来解决本题
已知△ABC∽△DEF,AB=6cm,DE="12cm," 且△ABC的周长为24cm,则△DEF的周长为 。
48 cm
题目分析:已知△ABC∽△DEF,所以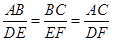 ,因为AB=6cm,DE=12cm,所以
,因为AB=6cm,DE=12cm,所以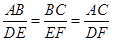 =
=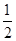 ,又因为△ABC的周长为24cm,即AB+BC+CA=24;则△DEF的周长=DE+EF+DF=2(AB+BC+CA)=48
,又因为△ABC的周长为24cm,即AB+BC+CA=24;则△DEF的周长=DE+EF+DF=2(AB+BC+CA)=48
点评:本题考查相似三角形,解答本题的关键是掌握相似三角形的性质,运用其性质来解决本题