问题
选择题
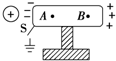
如图所示,把一个架在绝缘支架上的枕形导体放在正电荷形成的电场中.导体处于静电平衡时,下列说法不正确的是( )
A.A、B两点场强相等,且都为零
B.A、B两点场强不相等
C.感应电荷产生的附加电场EA>EB
D.当电键S闭合时,电子从大地沿导线向导体移动
答案
A、枕形导体在点电荷附近,出现静电感应现象,导致电荷重新分布.因此在枕形导体内部出现感应电荷的电场,正好与点电荷的电场叠加,内部电场强度处处为零,故A正确.
B、A、B两点场强相等,且都为零,故B错误.
C、点电荷的产生电场在A点的场强大于在B点的场强,在枕形导体内部出现感应电荷的电场,正好与点电荷的电场叠加,叠加后电场为零,所以感应电荷产生的附加电场EA>EB故C正确.
D、当电键S闭合时,电子从大地沿导线移向导体中和枕形导体右端的正电荷,相当于右端正电荷流向远端,故D正确.
本题选错误的,故选B.
