问题
丝绸之路示意图,回答下列问题。
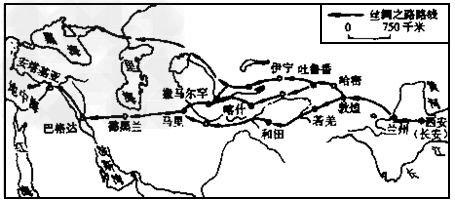
(1)写出丝绸之路的具体路线。
___________________________________________________________________
(2)它出现在什么时期?在我国历史上有哪些作用?
___________________________________________________________________
(3)西域是指我国今天的什么地区?西域与丝绸之路的关系怎样?
___________________________________________________________________
答案
(1)长安—河西走廊—西亚、中亚、南亚—大秦。
(2)西汉 它加强了中西联系,促进了东西方之间经济文化交流。
(3)新疆;丝绸之路通过西域,西域设置的都护府为丝绸之路的畅通提供了可靠的保证。