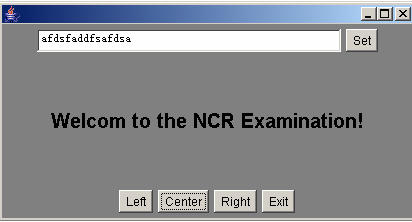
简单应用题请完成下列Java程序:制作一个图形用户界面,上方包含一个TextField和Button构件,实现输入字符串,点击Button获取文本区的字符;中间显示Label的内容;下方是4个按钮,分别实现控制Label在最左边,在中间,在右边和退出程序的功能。注意:请勿改动main( )主方法和其他已有语句内容,仅在下划线处填入适当的语句。程序运行结果如下:
 import java.awt.*;import java.awt.event.*;public class ex15_2 extends Frame implements ActionListener { private Label l; private TextField tf; public static void main(String[] arg) { ex15_2 obj15_2 = new ex15_2(); } public ex15_2() {setBackground(Color.gray); l = new Label("Welcom to the NCR Examination!"); Font font = new Font("TimesRoman",Font.BOLD,20); l.setFont(font); add("Center",l); Panel p = new Panel(); Button b = new Button("Left"); b.addActionListener(this); p.add(b); b = new Button("Center"); b.addActionListener(this); p.add(b); b = new Button("Right"); b.addActionListener(this); p.add(b); b = new Button("Exit"); b.addActionListener(this); p.add(b); ; p = new Panel(); tf = new TextField(40); p.add(tf); b = new Button("Set"); b.addActionListener(this); p.add(b); add("North",p); setSize(500,300); show(); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae) { if(ae.getActionCommand().equals("Exit")) System.exit(0); else if(ae.getActionCommand().equals("Left")) ;else if(ae.getActionCommand().equals("Center")) l.setAlignment(Label.CENTER); else if(ae.getActionCommand().equals("Right")) l.setAlignment(Label.RIGHT); else if(ae.getActionCommand().equals("Set")) l.setText(tf.getText()); }}
import java.awt.*;import java.awt.event.*;public class ex15_2 extends Frame implements ActionListener { private Label l; private TextField tf; public static void main(String[] arg) { ex15_2 obj15_2 = new ex15_2(); } public ex15_2() {setBackground(Color.gray); l = new Label("Welcom to the NCR Examination!"); Font font = new Font("TimesRoman",Font.BOLD,20); l.setFont(font); add("Center",l); Panel p = new Panel(); Button b = new Button("Left"); b.addActionListener(this); p.add(b); b = new Button("Center"); b.addActionListener(this); p.add(b); b = new Button("Right"); b.addActionListener(this); p.add(b); b = new Button("Exit"); b.addActionListener(this); p.add(b); ; p = new Panel(); tf = new TextField(40); p.add(tf); b = new Button("Set"); b.addActionListener(this); p.add(b); add("North",p); setSize(500,300); show(); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent ae) { if(ae.getActionCommand().equals("Exit")) System.exit(0); else if(ae.getActionCommand().equals("Left")) ;else if(ae.getActionCommand().equals("Center")) l.setAlignment(Label.CENTER); else if(ae.getActionCommand().equals("Right")) l.setAlignment(Label.RIGHT); else if(ae.getActionCommand().equals("Set")) l.setText(tf.getText()); }}
参考答案:add("South",p)l.setAlignment(Label.LEFT)
解析:本题主要考查AWT基本构件Button, Pane, Label和TextField结合的简单应用。解题关键是熟悉这几种基本构件一般用法,会设置Label在窗口中的位置。本题中,第1个空,将面板构件放在窗口的最下方;第2个空,根据Button事件调用l对象的setAlignment()方法,设置Label在面板中的位置。
