问题
单项选择题
酵母菌在有氧时进行有氧呼吸,无氧时进行无氧呼吸,将酵母菌放在含有培养液的半封闭锥形瓶中,测得CO2的释放量比O2的吸收量大1倍,则有氧呼吸与无氧呼吸消耗葡萄糖的比为:()
A.1:6
B.1:3
C.1:2
D.1:1
答案
参考答案:B
解析:
1mol葡萄糖在有氧呼吸时消耗6mol氧气,释放6mol二氧化碳,无氧呼吸时释放2mol二氧化碳,设消耗的氧气量为x,则有氧呼吸消耗的葡萄糖为x/6,释放的二氧化碳为x,则无氧呼吸释放的二氧化碳为x,消耗的葡萄糖为x/2,所以有氧呼吸与无氧呼吸消耗葡萄糖的比为1:3.
考点:本题考查细胞呼吸相关知识,意在考查考生识记所列知识点,并能运用所学知识做出合理的判断或得出正确的结论的能力。

 。关于
。关于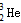 的说法不正确的是 [ ]
的说法不正确的是 [ ]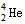 互为同位素
互为同位素 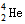 少一个电子
少一个电子