问题
选择题
读某气象站(1oN,35oE,海拔1875米)气候资料,据此回答下列各题。
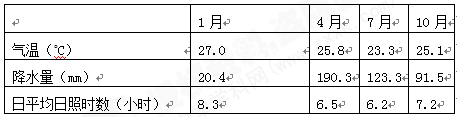
小题1:该气象站所在地的气候类型是( )
A.热带雨林气候
B.热带草原气候
C.热带季风气候
D.热带沙漠气候小题2:该气象站1月日平均日照时数高于7月,主要是因为该地1月( )
A.正午太阳高度大
B.白昼时间长
C.太阳辐射强
D.晴朗天气多
答案
小题1:B
小题2:D
题目分析:
小题1:根据经纬度判断,该地位于东非高原。根据表格中数据判断,该地全年高温,为热带地区,从降水量分配看,降水量有明显的季节变化,所以只能是热带草原气候。B对。热带雨林气候全年降水量大,降水量季节变化小,该地1月、7月的降水量差距大,A错。在非洲没有季风气候分布,C错。该地降水较多,不可能是沙漠气候,D错。
小题2:日照时数与当地的天气状况密切相关。读表格数据,该地1月降水量20.4mm,降水少晴天多,所以日照时数多;7月降水量123.3mm,降水多,阴天多,所以日照时数少;D对。正午太阳高度主要影响日照强度 ,不是日照时数的主要影响因素,A错。该地位于北半球,1月白昼时间比7月白昼时间短,B错。北半球,夏季太阳辐射比冬季强,C错。
