问题
解答题
一直线过抛物线y2=2px(p>0)的焦点F,且交抛物线于A,B两点,C为抛物线准线的一点.
(1)求证:∠ACB不可能是钝角;
(2)是否存在这样的点C,使得△ABC为正三角形?若存在,请求出点C的坐标;若不存在,请说明理由.
答案
解:设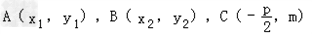 ,
,
直线AB方程为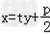
由 ,得:y2﹣2pty﹣p2=0,
,得:y2﹣2pty﹣p2=0,
则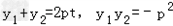
∴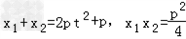 .
.
 ,
,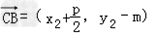
∴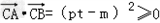
∴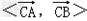 不可能为钝角,
不可能为钝角,
故∠ACB不可能是钝角
(2)假设存在点C,使得△ABC为正三角形
由(1)得:线段AB的中点为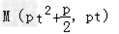
①若直线AB的斜率不存在,这时t=0,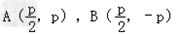 ,
,
点C的坐标只可能是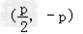 ,
,
由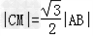 ,得:
,得: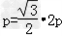 ,矛盾,
,矛盾,
于是直线AB的斜率必存在.
②由CM⊥AB,得:kCMkAB=﹣1,
即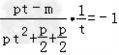 ,
,
∴m=pt3+2pt,
∴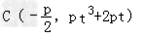
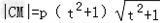 ,|AB|=2p(t2+1),
,|AB|=2p(t2+1),
由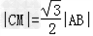 ,得:
,得: ,
,
∴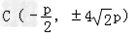
故存在点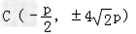 ,使得△ABC为正三角形.
,使得△ABC为正三角形.
