如下图所示,某园区网用2.5Gbps的POS技术与Internet相连,POS接口的帧格式是SONET。路由协议的选择方案是,园区网内部采用OSPF协议,园区网与Internet的连接使用静态路由。
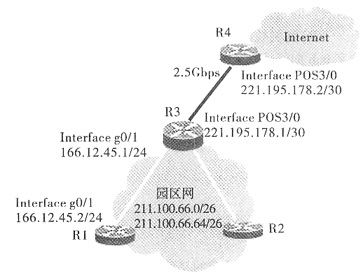
请阅读以下R1和R3的部分配置信息,并补充空白处的配置命令或参数,按题目要求完成路由器的配置。
R1缺省路由的配置信息如下:
Router-R1#configure terminal
Router-R1(config)#
Router-R1(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 ______
Router-R1(config)#exit
Router-R1#
R3的POS接口和OSPF协议的配置信息如下:
Router-R3#confgure terminal
Router-R3(config)#
Router-R3(config)#interface pos3/0
Router-R3(config-if)#description To Internet
Router-R3(config-if)#bandwidth 2500000
Router-R3(config-if)#ip address 221.195.t78.1 255.255.255.252
Router-R3(config-if)#crc 32
Router-R3(config-if)#pos ______
Router-R3(config-if)#no ip directed-broadcast
Router-R3(config-if)#pos flag ______
Router-R3(config-if)#no shutdown
Router-R3(config-if)#exit
Router-R3(config)#router ospf 65
Router-R3(config-router)#network 211.100.66.0 ______ area 0
Router-R3(config-router)#redistribute connected metric-type 1 subnets
Router-R3(config-router)#area 0 range 211.100.66.0 ______
Router-R3(config-router)#exit
Router-R3(config)#
参考答案:255.255.255.128
解析: 网络地址块211.100.66.0/26和211.100.66.64/26聚合后的地址块为211.100.66.0/25。该地址块为路由器R3配置OSPF的子网地址。在路由器的OSPF配置模式下,使用“network ip<子网号><wildeard.mask>area<区域号>”命令定义参与OSPF的子网地址,或使用“area<区域号>range<子网地址><子网掩码>”命令定义某一特定范围予网的聚合。注意network命令中的“<wildeard-mask>”是子网掩码的反码,即反掩码,如掩码为255.255.0.0,其反码应为0.0.255.255。本题中9处应填写子网掩码的反码,子网掩码是255.255.255.128;则反码是0.0.0.127。area命令中使用子网掩码,应为:255.255.255.128。故应填入:255.255.255.128。
