问题
实验题
探究声音的特性时,进行如下实验:
实验1:先拨动张紧的细橡皮筋,再拨动张紧的粗橡皮筋,观察先后两次发声时橡皮筋振动动快慢及声音的特点,记录如下表:
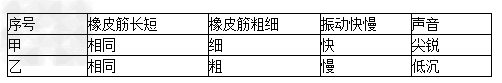
实验2:把音叉插入水中,留音叉柄在水面之外,两次敲打音叉溅起水花,第一次轻敲音叉,发现溅起的水花较小;第二次重敲音叉,发现溅起的水花较大,而且音叉两次发出的声音前者小些,后者大多了。
分析上述实验,回答下列问题:
(1)实验①主要研究声音的 与发声物体的振动 有关,即 越大,则 越高;
(2)实验②主要研究声音的 与发声物体振动的 有关,即 越大,则 越大。
答案
(1)音调;频率;频率;音调
(2)响度;幅度;振幅;响度
