问题
解答题
某商店欲购进甲、乙两种商品,已知甲的进价是乙的进价的一半,进3件甲商品和1件乙商品恰好用200元.甲、乙两种商品的售价每件分别为80元、130元,该商店决定用不少于6710元且不超过6810元购进这两种商品共100件.
(1)求这两种商品的进价.
(2)该商店有几种进货方案?哪种进货方案可获得最大利润,最大利润是多少?
答案
(1)商品的进价为40元,乙商品的进价为80元。
(2)有三种进货方案:
方案1,甲种商品30件,乙商品70件;
方案2,甲种商品31件,乙商品69件;
方案3,甲种商品32件,乙商品68件。
方案1可获得最大利润,最大=4700。
分析:(1)设甲商品的进价为x元,乙商品的进价为y元,就有 ,3x+y=200,由这两个方程构成方程组求出其解即可。
,3x+y=200,由这两个方程构成方程组求出其解即可。
(2)设购进甲种商品m件,则购进乙种商品(100﹣m)件,根据不少于6710元且不超过6810元购进这两种商品100的货款建立不等式,求出其值就可以得出进货方案,设利润为W元,根据利润=售价﹣进价建立解析式就可以求出结论。
解:(1)设甲商品的进价为x元,乙商品的进价为y元,由题意,得
 ,解得:
,解得: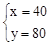 。
。
答:商品的进价为40元,乙商品的进价为80元。
(2)设购进甲种商品m件,则购进乙种商品(100﹣m)件,由题意,得
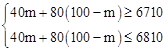 ,解得:
,解得: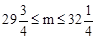 。
。
∵m为整数,∴m=30,31,32。
∴有三种进货方案:
方案1,甲种商品30件,乙商品70件;
方案2,甲种商品31件,乙商品69件;
方案3,甲种商品32件,乙商品68件。
设利润为W元,由题意,得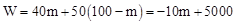 ,
,
∵k=﹣10<0,∴W随m的增大而减小。
∴m=30时,W最大=4700。
