问题
多项选择题
戊注册会计师负责对E公司2011年度财务报表进行审计,在审计过程中遇到下列有关应付账款审计的问题,请代为作出正确的专业判断。
根据E公司的实际情况,注册会计师可以选择以下方法对应付账款执行实质性分析程序的有( )。
A.分析存货和营业成本等项目的增减变动,判断应付账款增减变动的合理性
B.检查与应付账款有关的供应商发票、验收报告或入库单
C.将期末应付账款余额与期初余额进行比较,分析波动原因
D.分析长期挂账的应付账款,要求E公司作出解释,判断被审计单位是否缺乏偿债能力或利用应付账款隐瞒利润;并注意其是否可能无须支付,对确定无须支付的应付款的会计处理是否正确,依据是否充分
答案
参考答案:A,C,D
解析: 选项B是检查应付账款是否存在未及时入账,确认应付账款期末余额完整性所用的程序,不属于应付账款的分析程序。除了上述A、C、D三项分析程序外,注册会计师对应付账款进行分析程序还可以是计算应付账款与存货的比率,应付账款与流动负债的比率,并与以前年度相关比率对比分析,评价应付账款整体的合理性。

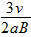 ,正电荷
,正电荷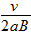 ,正电荷
,正电荷 ,负电荷
,负电荷 ,负电荷
,负电荷