问题
材料分析题
阅读下列材料,回答问题:
材料一:我国某地理科考队对非洲大陆地形、气候、热带草原区的农牧业生产和环境等方面进行了科学考察。
材料二:非洲沿赤道地形剖面图和东非裂谷带图

(1)读非洲沿赤道地形剖面图,填出序号代表的地理事物名称:
①_______洋,②_______高原,③_______盆地,④_________洋。
(2)考察队员发现非洲裂谷带底部有狭长而深陷的谷地和湖泊,附近火山、地震活动频繁,该裂谷的成因是_________________________________________。
(3)考察队员站在乞力马扎罗山麓地带,测得海拔高度是500米,气温是20℃,该山顶部的气温应该是_______℃。
(4)考察队员发现热带草原 农业区人口增长快,土地荒漠化严重。请把下图中的数字与内容序号合理搭配,并填在题目下方:
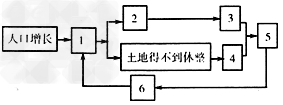
A.土壤肥力下降
B.恶性循环
C.开垦草原
D.要求增加粮食产量
E.土地沙化严重
F.粮食产量下降
1______,2______,3______,4______,5_______,6_______。(只填字母)
答案
(1)印度;东非 刚果;大西
(2)板块张裂而成
(3)-12.37
(4)D;C;E;A;F;B
