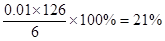(12分) 实验室可由软锰矿(主要成分为 MnO2)制备 KMnO4,方法如下:软锰矿与过量固体 KOH 和 KClO3在高温下反应,生成锰酸钾(K2MnO4)和 KCl;用水溶解,滤去残渣,滤液酸化后,K2MnO4转变为MnO2和 KMnO4;滤去MnO2沉淀,浓缩滤液,结晶得到深紫色的针状KMnO4请回答:
(1)软锰矿制备K2MnO4的化学方程式是 。
(2)K2MnO4制备KMnO4的离子方程式是 。
(3)配平氧化还原反应方程式:
__ C2O42-+__MnO4-+__H+=__CO2+__Mn2++__H2O
(4)称取6.0 g含H2C2O4·2H2O、KHC2O4和K2SO4的试样,加水溶解,配成250mL溶液。量取两份此溶液各25.00 mL,分别置于两个锥形瓶中。
①第一份溶液中加入酚酞试液,滴加0.25 mol·L-1NaOH溶液至20.00 mL时,溶液由无色变为浅红色。该溶液被中和的H+的物质的量为___mol。
②第二份溶液中滴加0.10 mol·L-1的酸性高锰酸钾溶液至16.00 mL时反应完全,此时溶液颜色由__变为__。该溶液中还原剂的物质的量为___mol。
③原试样中H2C2O4·2H2O的质量分数为_____。
(1)3MnO2+6KOH+KClO3=3K2MnO4+KCl+3H2O(2分)
(2)3MnO42-+4H+=MnO2+2MnO4-+2H2O(2分) (3)5 2 16 10 2 8(2分)
(4)①0.005(1分) ②无色(1分) 橙红色(1分) 0.004 (1分)③ 21% (2分)
(1)根据原子守恒可知,含有水生成。再依据电子的得失守恒可知,方程式为3MnO2+6KOH+KClO3=3K2MnO4+KCl+3H2O
(2)在酸性条件下,锰酸钾生成二氧化锰和高锰酸钾,根据原子守恒可知,还有水生成,因此该反应的方程式是3MnO42-+4H+=MnO2+2MnO4-+2H2O。
(3)根据方程式可知,Mn元素的化合价从+7价降低到+2价,得到5个电子。碳元素的化合价从+3价升高到+4价,失去1个电子,所以根据电子的得失守恒可知,氧化剂和还原剂的物质的量之比是2︰5,因此系数分别是5 2 16 10 2 8。
(4)①氢氧化钠的物质的量是0.25 mol·L-1×0.020L=0.005mol,所以被中和的氢离子也是0.005mol。
②由于酸性高锰酸钾溶液显紫红色,所以终点时的现象是溶液颜色由无色变为紫红色。消耗高锰酸钾是0.0016mol,所以根据方程式可知,还原剂的物质的量是0.004mol。
③设H2C2O4·2H2O、KHC2O4的物质的量分别是和x和y,则x+y=0.004mol×10,2x+y=0.005mol×10,解得x=0.01mol,y=0.03mol,所以原试样中H2C2O4·2H2O的质量分数为