问题
选择题
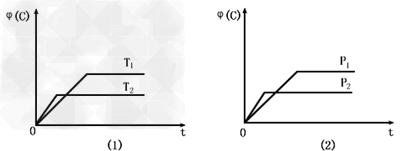
可逆反应mA(s)+nB(g)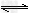 pC(g)+qD(g)反应过程中,当其他条件不变时,C的体积分数Φ(C)在不同温度(T)和不同压强(P)的条件下随时间(t)的变化关系如图所示。 下列叙述正确的是
pC(g)+qD(g)反应过程中,当其他条件不变时,C的体积分数Φ(C)在不同温度(T)和不同压强(P)的条件下随时间(t)的变化关系如图所示。 下列叙述正确的是
A.达到平衡后,若使用催化剂,C的体积分数将增大
B.当平衡后,若温度升高,化学平衡向逆反应方向移动
C.化学方程式中,n>p+q
D.达到平衡后,增加A的质量有利于化学平衡向正反应方向移动
答案
答案:B
