问题
问答题
下表是元素周期表的一部分,表中的每个字母表示一种短周期元素,回答下列问题:

(1)画出C的原子结构示意图______.
(2)E在元素周期表中的位置是第3周期______族.
(3)B、C、D、F四种元素所形成的气态氢化物最稳定的是______(填化学式).
(4)E、F、G元素的最高价氧化物对应水化物的酸性最强的是______(填化学式).
(5)A、B、G三元素形成的化合物的电子式是______,其中所含的化学键有哪些类型______.
答案
(1)C为O元素,原子序数为8,原子核外有两个电子层,最外层电子数为6,则原子结构示意图为
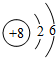
,
故答案为:
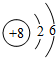
;
(2)E为P元素,原子序数为15,核外有3个电子层,最外层电子数为5,则位于周期表第三周期ⅤA族,
故答案为:第ⅤA;
(3)B、C、D、F四种元素中非金属性最强的是F元素,对应的氢化物的稳定性最强,故答案为:HF;
(4)同周期元素从左到右元素的非金属性逐渐增强,对应的最高价氧化物的水化物的酸性逐渐增强,故答案为:HClO4;
(5)A、B、G三元素形成的化合物为NH4Cl,为离子化合物,含有离子键和共价键,
电子式为
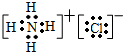
,
故答案为:
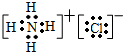
;离子键和共价键.
