问题
选择题
甲站在岸上,乙潜入清澈的水中站立,二人互相对看.甲、乙看到对方的头部位置
A.都比实际位置高
B.都比实际位置低
C.甲看乙低,乙看甲高(与实际位置比较)
D.甲看乙高,乙看甲低(与实际位置比较)
答案
答案:A
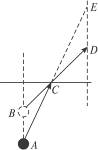
如图所示,A为水中的人,D为岸上的人,D看到的A发出的光线为CD,所以A的像为B,变高.根据光的可逆性原理,A看到的D的像为E,也变高了.
甲站在岸上,乙潜入清澈的水中站立,二人互相对看.甲、乙看到对方的头部位置
A.都比实际位置高
B.都比实际位置低
C.甲看乙低,乙看甲高(与实际位置比较)
D.甲看乙高,乙看甲低(与实际位置比较)
答案:A
如图所示,A为水中的人,D为岸上的人,D看到的A发出的光线为CD,所以A的像为B,变高.根据光的可逆性原理,A看到的D的像为E,也变高了.
