MnSO4·H2O在工业、农业等方面有广泛的应用。工业上用化工厂尾气中低浓度SO2还原MnO2矿制备MnSO4·H2O过程如下:

已知: 常温时部分硫化物难溶盐的Ksp:CuS--6.3×10-36、PbS--1.0×10-28、NiS--2.0×10-26、
MnS--2.5×10-10,请回答下列问题:
(1)生产中MnO2矿粉碎的目的是 。
(2)除铁发生的离子反应方程式为 。
(3)除重金属离子后,若混合溶液中Cu2+、Pb2+、Ni2+的浓度均为1.0×10-5mol/L,则c(S2-)最大= mol/L。
(4)已知MnSO4·H2O在1150℃高温下分解的产物是Mn3O4、含硫化合物、水,则在该条件下硫酸锰晶体分解反应的化学方程式是
(12分)(1)增大反应物接触面积,加快反应速率; (3分)
(2)2Fe3+ + 3H2O + 3CaCO3 = 2Fe(OH)3↓+ 3CO2↑+ 3Ca2+ (3分)
(或 Fe3+ + 3H2O = Fe(OH)3↓+ 3H+ 2H+ + CaCO3 = Ca2+ + CO2↑+ H2O )
(3)6.3×10-31 (3分) (4)3MnSO4·H2O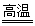 Mn3O4 + SO2↑+ 2SO3↑+ 3H2O (3分)
Mn3O4 + SO2↑+ 2SO3↑+ 3H2O (3分)
题目分析:(1)生产中MnO2矿粉碎增大了反应物的接触面积,加快了化学反应速率,即答案为:增大反应物接触面积,加快反应速率。
(2)溶液中溶解度大的物质向溶解度小的物质转化,碳酸钙的溶度积大于氢氧化铁的溶度积,所以在水溶液里,铁离子和碳酸钙反应生成氢氧化铁,离子方程式为2Fe3+ + 3H2O + 3CaCO3 = 2Fe(OH)3↓+ 3CO2↑+ 3Ca2+。
(3)当溶液中溶度积最小的物质恰好饱和时硫离子的浓度才最大,溶度积最小的是CuS--6.3×10-36,当溶液中Cu2+为1.0×10-5mol/L,则c(S2-)最大=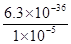 =6.3×10-31 mol/L。
=6.3×10-31 mol/L。
(4)MnSO4•H2O在1150℃高温下分解的产物是Mn3O4、含硫化合物、水。生成Mn3O4锰元素失电子,生成二氧化硫是得电子,根据氧化还原反应中得失电子数相等结合原子守恒得出反应方程式为
3MnSO4·H2O Mn3O4 + SO2↑+ 2SO3↑+ 3H2O。
Mn3O4 + SO2↑+ 2SO3↑+ 3H2O。
点评:该题以制备MnSO4·H2O为载体,重点考查学生对工艺流程试题了解掌握情况。试题综合性强,贴近高考,侧重对学生能力的培养和训练,有利于培养学生的逻辑推理能力和规范严谨的实验设计能力以及动手操作能力。该类试题综合性强,理论和实践的联系紧密,有的还提供一些新的信息,这就要求学生必须认真、细致的审题,联系所学过的知识和技能,进行知识的类比、迁移、重组,全面细致的思考才能得出正确的结论。该题的易错题是(3),明确当溶度积最小的都不产生沉淀时,硫离子的浓度才最大,这样才能作出正确解答。

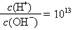 的溶液中:NH4+、Ca2+、Cl-、K+
的溶液中:NH4+、Ca2+、Cl-、K+