问题
实验题
某同学设计了一个用打点计时器探索碰撞中不变量的实验:在小车A的前端装有橡皮泥,推动小车A使之匀速运动,然后与原来静止在前方的小车B相碰并粘合成一体,继续做匀速运动,他设计的装置如图所示,在小车A的后面连着纸带,电磁打点计时器电源频率为50 Hz,长木板的一端下垫着小木片用以平衡摩擦力。

(1)若已得到打点纸带如图所示,并测得各计数点间距标在下图上,A为运动起始的第一个点,则应选________段来计算A碰前速度,应选________段来计算A和B碰后的共同速度。
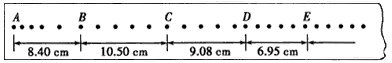
(2)已测得小车A质量为m1=0.40 kg,小车B的质量为m2=0.20 kg,由以上测量可得:
碰前两车质量与速度乘积之和=________kg·m/s;
碰后两车质量与速度乘积之和=________kg·m/s。
(3)结论____________________________________________。
答案
(1)BC,DE
(2)0.420,0.417
(3)在误差允许的范围内,碰前的质量与速度乘积之和等于碰后的质量与速度乘积之和,即碰撞过程中的不变量为质量与速度乘积之和
