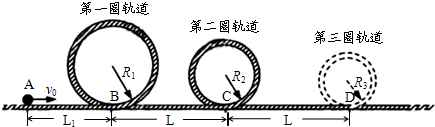
过山车是游乐场中常见的设施.下图是一种过山车的简易模型,它由水平轨道和在竖直平面内的三个圆形轨道组成,B、C、D分别是三个圆形轨道的最低点,B、C间距与C、D间距相等,半径R1=2.0m、R2=1.4m.一个质量为m=1.0kg的小球(视为质点),从轨道的左侧A点以v0=12.0m/s的初速度沿轨道向右运动,A、B间距L1=6.0m.小球与水平轨道间的动摩擦因数为0.2,圆形轨道是光滑的.假设水平轨道足够长,圆形轨道间不相互重叠.重力加速度取g=10m/s2,计算结果保留小数点后一位数字.试求
(1)小球在经过第一个圆形轨道的最高点时,轨道对小球作用力的大小;
(2)如果小球恰能通过第二圆形轨道,B、C间距L应是多少;
(3)在满足(2)的条件下,如果要使小球不能脱离轨道,在第三个圆形轨道的设计中,半径R3应满足的条件;小球最终停留点与起点A的距离.
(1)设小球经过第一个圆轨道的最高点时的速度为v1根据动能定理得:
-μmgL1-2mgR1=
mv12-1 2
mv02 ①1 2
小球在最高点受到重力mg和轨道对它的作用力F,根据牛顿第二定律有:
F+mg=m
②v 21 R1
由 ①、②得 F=10.0 N ③
(2)设小球在第二个圆轨道的最高点的速度为v2,由小球恰能通过第二圆形轨道有:
mg=m
④v 22 R2
-μmg(L1+L)-2mgR2=
mv22-1 2
mv02 ⑤1 2
由④、⑤得 L=12.5m ⑥
(3)要保证小球不脱离轨道,可分两种情况进行讨论:
I.轨道半径较小时,小球恰能通过第三个圆轨道,设在最高点的速度为v3,应满足
mg=m
⑦v 23 R3
-μmg(L1+2L)-2mgR3=
mv32-1 2
mv02 ⑧1 2
由 ⑥、⑦、⑧得 R3=0.4m
II.轨道半径较大时,小球上升的最大高度为R3,根据动能定理
-μmg(L1+2L)-2mgR3=0-
mv02 1 2
解得 R3=1.0m
为了保证圆轨道不重叠,R3最大值应满足
(R2+R3)2=L2+(R3-R2)2
解得 R3=27.9m
综合I、II,要使小球不脱离轨道,则第三个圆轨道的半径须满足下面的条件
0<R3≤0.4m或 1.0m≤R3≤27.9m
当0<R3≤0.4m时,小球最终焦停留点与起始点A的距离为L′,则
-μmgL′=0-
mv02 1 2
L′=36.0m
当1.0m≤R3≤27.9m时,小球最终焦停留点与起始点A的距离为L〞,则
L″=L′-2(L′-L1-2L)=26.0m
答:(1)小球在经过第一个圆形轨道的最高点时,轨道对小球作用力的大小为10.0N;
(2)如果小球恰能通过第二圆形轨道,B、C间距L应是12.5m;
(3)第三个圆轨道的半径须满足下面的条件 0<R3≤0.4m或 1.0m≤R3≤27.9m
当0<R3≤0.4m时,小球最终焦停留点与起始点A的距离为36.0m
当1.0m≤R3≤27.9m时,小球最终焦停留点与起始点A的距离为26.0m.
