问题
选择题
如图所示,两条虚线之间的部分表示生态系统功能正常的作用范围。y表示一个外来干扰使之偏离这一范围的大小;x表示恢复到原状态所需的时间;曲线与正常范围之间所夹的面积可以作为总稳定性的定量指标(TS)。下列说法正确的是
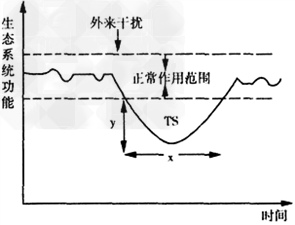
A.在正常作用范围内,生态系统中生物的种类和数量保持不变
B.在遭到干扰时,x、y值的大小与生物的种类有关,与数量无关
C.一般来说,对同一个生态系统,y值和x值之间呈负相关
D.TS值越小,这个生态系统的总稳定性越大
答案
答案:C
