第一节 完形填空(共10小题;每小题2分,满分20分)
阅读下面短文,掌握其大意,然后从21—30各题所给的四个选项(A、B、C和D)中,选出最佳选项,并在答题卡上将该项涂黑。
Cars are too expensive for many people around the world to own. Not only that, many cities are already full of traffic, and many country areas have rough roads.
So how do people 21 those distances that are too far to walk? They use public transportation. If you ride the subway 22 bus where you live, you can appreciate some of the benefits of public transportation. With many people 23 one bus or train there is less traffic and, more importantly, less 24 .
Which of the types of mass transit described below are you familiar with? If a regular bus can 25 dozens of people, imagine what a bus twice the size can hold! In Great Britain, there are many buses that are 26 double-deckers.
Buses in Haiti are often very crowded. It’s not 27 for passengers to actually sit on the rooftops. Buses are sometimes called “tap-taps”, because the riders on the roof tap(敲击)when they want to be dropped off.
Many large cities around the world take advantage of the 28 beneath the streets and run underground trains. People in Paris, Mexico City and Tokyo may use the subway system to get to school, to work, or to visit friends in other neighborhoods. Both the Japanese and French have 29 High-speed trains to link various cities. While electric trains in North America 30 130 kph, the French TGV (high-speed-train) is the world’s fastest, averaging over 270 kph!
21. A. find B. fly C. observe D. travel
22. A. and B. also C. or D. as well as
23. A. sharing B. crowding C. sparing D. sitting
24. A. smoke B. people C. buses D. pollution
25. A. include B. stand C. hold D. seat contain
26. A. known as B. popular with C. familiar with D. looked like
27. A. frequent B. usual C. true D. uncommon
28. A. building B. structure C. space D. channel
29. A. imported B. operated C. produced D. developed
30. A. travel B. average C. run D. fly

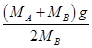 B.
B. 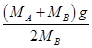 和0
和0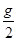 和0 D.都等于
和0 D.都等于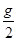
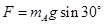 ,所以根据牛顿第二定律得:B的加速度为
,所以根据牛顿第二定律得:B的加速度为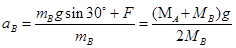 .故BCD错误,A正确.所以选D.
.故BCD错误,A正确.所以选D.