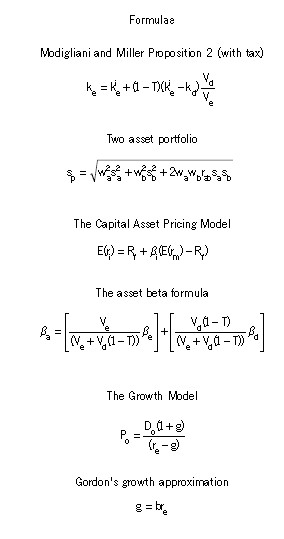
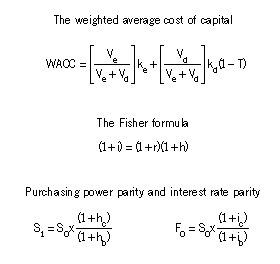
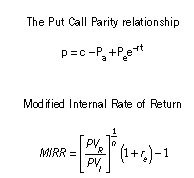
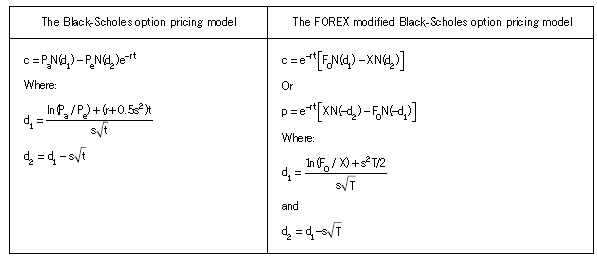
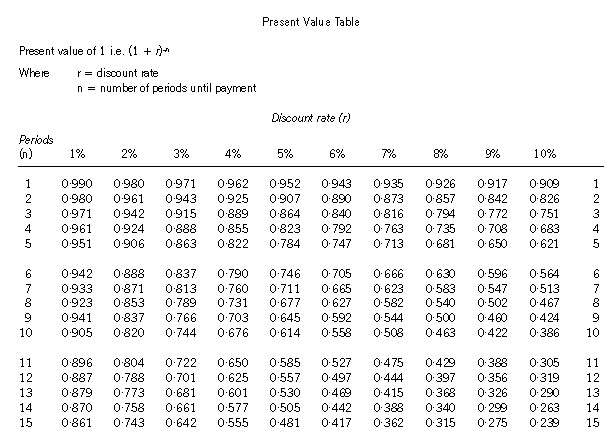
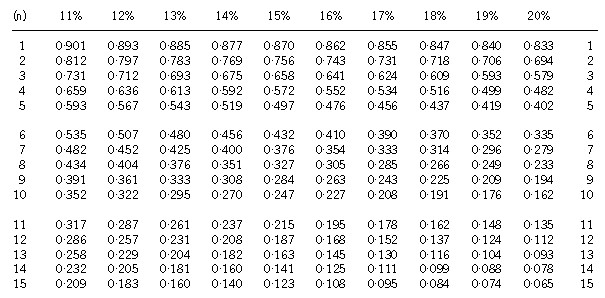
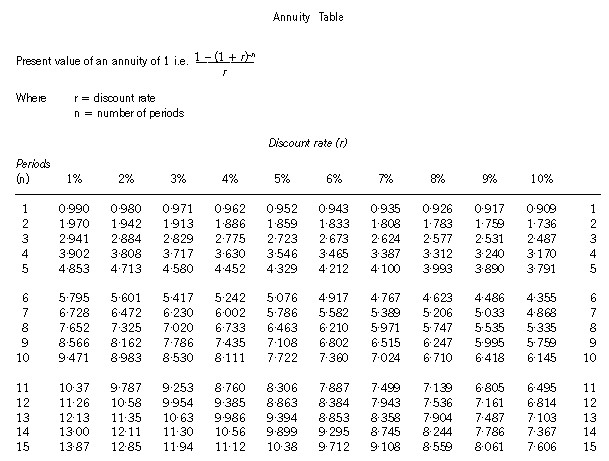
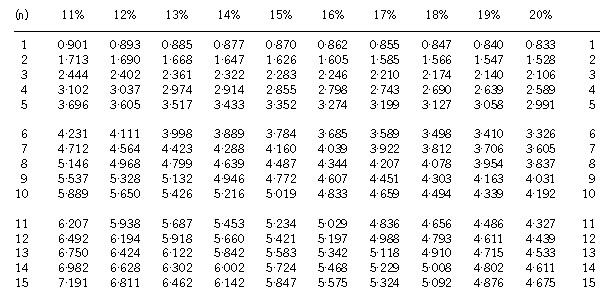
 Section A–BOTH questions are compulsory and MUST be attempted
Section A–BOTH questions are compulsory and MUST be attempted
参考答案:Up to D professional marks are available for the presentation of the answer, which should be in a report style.The decision should be taken in the best interests of the shareholders and other stakeholders of the company.Obviously all the input numbers should be considered on basis of their reasonableness and accuracy.Hence the positions of the interested parties will be considered on this basis.A. Cease Trading and Liquidate the CompanyThis is probably not in the best interest of any party. Debt holders only receive EE·Gc for every $A invested and the shareholders receive nothing (see appendix, proposal A). Furthermore, the parts division is continuing to make a profit and should possibly continue.The Board may want to consider closing just the fridge division, and focusing on the parts manufacturing division, with the possibility of pursuing the option of the mobile refrigeration business. However, in this case, the problem of the lack of funding might continue.B. Corporate Restructuring and Management Buy-OutShareholdersThe shareholders would benefit from either proposal two or three, as opposed to the first proposal, as they stand to gain some funds. The restructuring proposal requires them to pay $D0m cash for new shares but lose their control of the company (the shareholding falls to just under AC%). On the other hand the statement of financial position looks robust with a $B0m cash float and bank overdraft facilities probably available at previous levels (see appendix, proposal B). This may make the company more successful in the future, as directors are less restricted by covenants. The value at $BEF·Cm currently only gives existing shareholders a share (or stake) of about $CC·Cm (AC% x $BEF·Cm), which is less than the amount they would inject.The shareholders would benefit immediately if the management buy-out option is taken because they will receive a premium on the share price, although this may still be lower than when the company’s share price was at its height.Therefore the shareholders need to weigh up whether they would like to possibly benefit from future company prospects (not evident at the moment) or whether they would like to sell their shares for F0c per share. They would probably opt for the management buy-out.Unsecured Bond HoldersThe unsecured bond holders’ position is not dissimilar to the shareholders’ position in that with the restructuring, their financial position depends on the future success of the company, but with the management buy-out they benefit from receiving the full repayment of their initial investment. However, their preferred proposal is probably more difficult to judge.With the restructuring option they would become the majority shareholder with just over HG% of the company for a total investment of $BA0m. They would be able to play a major part in influencing the management’s decision possibly with representation on the Board. However, they would be exposed to additional risk as equity holders, as opposed to being debt holders.The value attributable to them based on perpetuity cash flows is $BBCm ($BEF·C x HG%) approximately, which is more than their investment. Like the shareholders they would benefit from any future projects that the re-structured business undertakes. They would also receive the shares at a significant discount, BG0m shares for $BA0m which is GG·Gc per $A par value. The ability to influence the Board and the possibility of obtaining a higher return than their investment from almost the start may sway them to accept the restructuring option. On the other hand, the management buy-out pays them what is due immediately, but they cannot participate in future benefits.Bond holders may therefore be more tempted to opt for the restructuring when compared to shareholders.Directors and Management Participating in the Management Buy-OutIf the restructuring is considered as opposed to liquidation then clearly a significant benefit to the management and directors is that they would retain their employment, unless the new shareholder owners decide to terminate some of their contracts.The possibility of the offer of the share options is interesting. At first the $A·A0 exercise price may seem generous as the directors would be able to exercise when the price of shares increase by just A0%. However, it is unlikely that the share price will start at $A per share. If the estimate of the value to perpetuity of $BEF·Cm is taken against the total number of shares of CA0m, this gives a theoretical share price of HB·Gc per share. This means that the share price needs to increase by over CC% before the option will become in-the-money. The option is currently well out-of-money and would have a low value. Given the asymmetric payoff of the option and the need to increase the price dramatically, directors and managers may be tempted to act in an excessively risky manner, to the detriment of the shareholders and other stakeholders. Indeed research has shown that the presence of share options in individual pay structure do make option holders behave in a more risky manner compared to pay structures which do not contain options.The management buy-out may influence different classes of managers and directors very differently. For those who participate in the management buy-out, the calculations seem to indicate a clear benefit (see appendix, proposal C) of a gain net of the cost of the buy-out. It would seem that by having a E% growth, the value has increased to more than E0% of the initial cost of the buy-out, although some unreasonable assumptions have been made. For managers and directors not participating in the buy-out, it is likely that they will lose their employment once the fridge division is sold.ConclusionGiven that the shareholders will probably prefer the management buy-out, and as it appears to have a significant advantage for the participating managers, it is likely that this will be the option that is preferred. Although some parties may not approve of the option, it is unlikely that their ‘voice’ will be strong enough to alter the decision.[*]The current and non-current liabilities will receive EE·Gc per $A owing to them (AEF/BH0). Shareholders will receive nothing.[*][*]Note: Even after the G% growth, the fridge division is still loss-making. Revenue = $CD0 x A·0G = $CFC·Hm, costs (unchanged)= $CG0m.[*][*]Note: It is assumed that, as before, the depreciation and the amount of capital investment needed are roughly equal. It is assumed that no additional investment in non-current assets or working capital is needed, even though sales revenue is increasing. It is assumed that additional initial working capital requirement is part of the new venture investment of $E0m.*It is assumed that C0% of the sales revenue lost due to the closure of the fridge division is not recovered.Cost of capital = AA%Estimated value based on cash flows to perpetuity = BH·D/(0·AA – 0·0E) = $DGC·CmThis is over E0% in excess of the funds invested in the new venture.C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\My Documents\图片\AB.jpgC:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\My Documents\图片\AA.jpgC:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\My Documents\图片\A0.jpgC:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\My Documents\图片\I.jpgC:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\My Documents\图片\H.jpg
