问题
单项选择题
A、B两辆火车同时从甲、乙两站相对开出,两车相遇后继续前进,到达对方车站。已知A车在相遇后所用的时间比相遇前所用的时间少l小时36分钟,B车在相遇后所用的时间比相遇前所用的时间多用2小时,并知A车每小时比B车快10千米。则两车的速度分别为多少千米/小时()
A.30,40
B.40,50
C.25,35
D.50,60
答案
参考答案:B
解析:
设B车速度为x千米/小时,则A车速度为(x+10)千米/小时。列方程2x=(x+10)×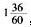 ,解得x=40千米/小时。所以两车速度分别为40千米/小时、50千米/小时。
,解得x=40千米/小时。所以两车速度分别为40千米/小时、50千米/小时。
