铬铁矿的主要成分的化学式为FeO·Cr2O3,还含有SiO2、Al2O3等杂质。工业上常采用固体碱熔氧化法用铬铁矿粉制备重铬酸钾,流程为:
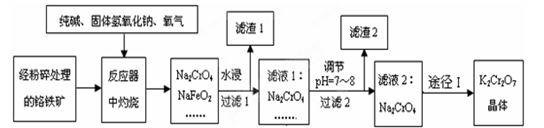
已知:①NaFeO2遇水强烈水解;
②重铬酸钾为橙红色针状晶体,溶于水,不溶于乙醇,有强氧化性;
③2CrO42- + 2H+ Cr2O72-+ H2O
Cr2O72-+ H2O
(1)灼烧操作一般在坩埚中进行,下列物质适合用来制作此实验坩埚材料的是
A.铁
B.氧化铝
C.石英
D.陶瓷(2)①铬铁矿经粉碎处理的目的是 。
②写出Cr2O3和纯碱、氧气反应生成Na2CrO4的化学方程式为 ;
③NaFeO2水浸时强烈水解生成氢氧化铁沉淀,离子方程式为___ ___。
(3)滤液1的成分除Na2CrO4、NaOH外,还含有(填化学式) ,
(4)通过途径Ⅰ从Na2CrO4溶液获得K2Cr2O7晶体,操作步骤有:“酸化”→加KCl固体→蒸发浓缩→操作a→过滤→洗涤→干燥。
① “酸化”步骤用醋酸调节溶液pH<5,其目的是 ;
②操作a的名称 。
(1)A ( 3分)
(2)① 增大反应物的表面积,加快反应速率(2分)
② 2Cr2O3 + 3O2+4Na2CO3  4Na2CrO4+4CO2↑(3分,未配平扣1分)
4Na2CrO4+4CO2↑(3分,未配平扣1分)
③ FeO2-+2H2O=Fe(OH)3↓+OH- (3分,未配平扣1分)
(3)NaAlO2 、Na2SiO3(2分)
(4)①使2CrO42- + 2H+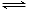 Cr2O72-+ H2O 的平衡向正反应方向移动,尽量将CrO42-转化为Cr2O72-(2分)
Cr2O72-+ H2O 的平衡向正反应方向移动,尽量将CrO42-转化为Cr2O72-(2分)
②冷却结晶(1分,只写冷却或只写结晶不得分)
题目分析:(1)陶瓷中含二氧化硅,石英的作用成分是二氧化硅,氢氧化钠与氧化铝、二氧化硅反应,所以适合用来制作此实验坩埚材料的是铁,答案选A;
(2)①粉碎固体使其与反应物的接触面积增大,加快反应速率;
② 根据元素守恒判断Cr2O3和纯碱、氧气反应生成Na2CrO4和二氧化碳,化学方程式为
2Cr2O3 + 3O2+4Na2CO3  4Na2CrO4+4CO2↑;
4Na2CrO4+4CO2↑;
③ NaFeO2水浸时强烈水解生成氢氧化铁沉淀,书写离子方程式时可逆符号变为“=”,离子方程式为
FeO2-+2H2O=Fe(OH)3↓+OH-
(3)SiO2、Al2O3等杂质与氢氧化钠反应生成硅酸钠、偏铝酸钠,所以滤液1的成分除Na2CrO4、NaOH外,还含有NaAlO2 、Na2SiO3
(4)①根据已知③Na2CrO4溶液中存在2CrO42- + 2H+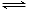 Cr2O72-+ H2O平衡,加入醋酸调节pH<5,使平衡正向移动,尽量将CrO42-转化为Cr2O72-
Cr2O72-+ H2O平衡,加入醋酸调节pH<5,使平衡正向移动,尽量将CrO42-转化为Cr2O72-
②由溶液得到晶体的一般步骤是加热浓缩、冷却结晶、过滤、洗涤、干燥,所以本实验中加热浓缩后应冷却结晶。