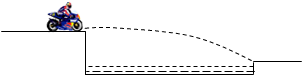
Many skilled young people are being forced into part-time and unskilled work, the report says. It warns of a "crisis" with more than six million people so disillusioned they have given up looking for work. The ILO(International Labor Organization)wants governments to make job creation a priority. It wants more training schemes, and also tax breaks for employers.
"The youth unemployment crisis can be beaten but only if job creation for young people becomes a key priority in policymaking and private sector investment picks up significantly," said Jose Manuel Salazar-Xirinachs, executive director of the ILO's employment sector.
Since 2007, the number of young people without jobs has risen by four million - up from less than 12%, the Global Employment Trends for Youth Report says. Almost 13% of people aged between 15 and 24 - or almost 75 million - have no work, although this is slightly down on its peak in 2009.
In the European Union, one in five young people are looking for work, the report claims. Some 27.9% of youths were unemployed in North Africa last year —a rise of five percentage points on 2010. In the Middle East, the figure stood at 26.5% in the report's regional breakdown. Even in East Asia, perhaps the most economically active region, the unemployment rate was 2.8 times higher for young people than for adults, the report said.
But, the ILO report reveals, the true picture of youth unemployment is even more pessimistic. Many young people are extending their time in higher education because they cannot find jobs. Others are taking part-time unskilled work because they cannot find work in the fields they trained for.
The ILO says that more than six million young people worldwide have given up looking for work and are becomingly increasingly detached from society. By not using their skills they are losing them, the report says, and if there is no improvement in the jobs market soon, they may be not only unemployed, but unemployable.
The ILO suggests offering tax breaks to businesses hiring young people and offering more programmes to help kick-start careers.
小题1:Which of the following is true according to Jose Manuel Salazar-Xirinachs?
A.Since 2007, the number of young people out of job has risen to 4 million.
B.Nearly 13% of the young people have no work.
C.Job creation should be made a key priority in policymaking.
D.The youth unemployment rate can never go down.小题2:The various figures in paragraph 3 and 4 were used to show_______.
A.The employment situation is serious only in the European Union
B.The global youth employment situation is depressing
C.East Asia enjoys a high youth employment rate
D.Compared with the situation in 2009, the youth employment in 2007 is slightly better小题3:According to ILO, the following are caused by high youth unemployment rate except_______.
A.The government calls on young people to take up whatever job is available
B.Many young people are making their time in higher education longer
C.Some young people are taking part-time unskilled work
D.Many young people have given up looking for work小题4:The ILO offered many solutions to the crisis of youth unemployment, including_______.
a. making job creations a priority b. more training schemes
c. encouraging public investment d. tax breaks for employers
e. offering more entrepreneurship programmes to help start careers
A.a b c e
B.b c d e
C.a c d e
D.a b d e

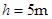 ,一辆摩托车(可看作质点)以
,一辆摩托车(可看作质点)以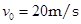 的水平速度向河对岸飞出,恰好越过小河.不计空气阻力,取当地的重力加速度
的水平速度向河对岸飞出,恰好越过小河.不计空气阻力,取当地的重力加速度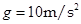 .试求:
.试求: