问题
选择题
读下图,回答1~4题。
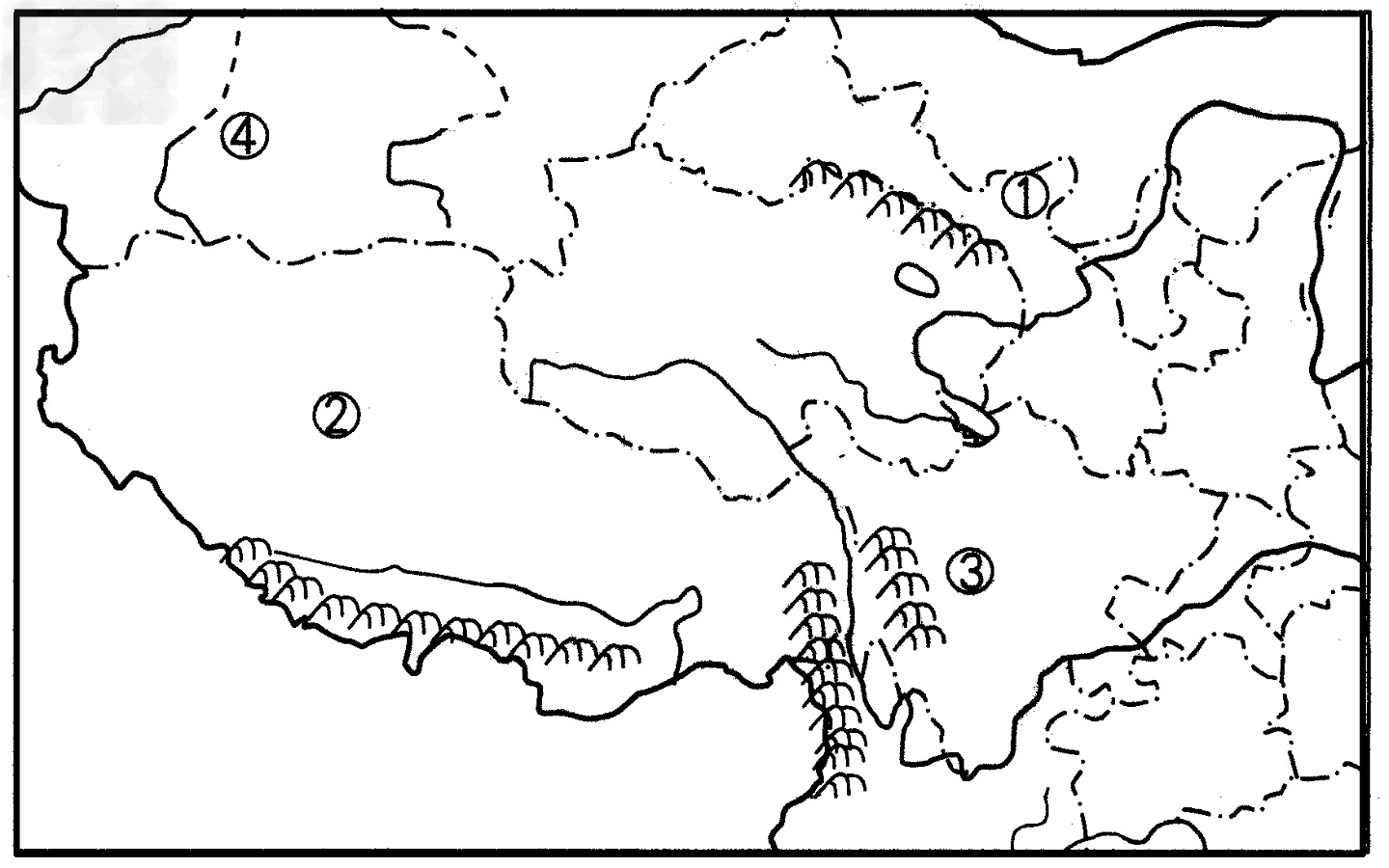
1.图中①和②处发展农业生产的主要制约因素分别是[ ]
A.地形、水源
B.水源、气温
C.水源、光照
D.土壤、地形
2.图中②所在的省区,丰富的可再生新能源主要有[ ]
A.太阳能、生物能
B.风能、石油
C.太阳能、地热能
D.地热能、天然气
3.图中③所示山区是我国第二大林区,但树种却比东北第一大林区丰富,其主要原因是③所示山区[ ]
A.年降水量大、气温高
B.光照和热量条件好
C.纬度低、海拔高
D.土壤肥沃、水源充足
4.图中④处所示地形单元的农业生产类型和重要农产品组合正确的是 [ ]
A.河谷灌溉农业——小麦
B.绿洲灌溉农业——棉花
C.温带草原畜牧业——细毛羊
D.山地畜牧业——滩羊
答案
1、B
2、C
3、C
4、B
