认真阅读下列短文,根据所读内容在文章后表格中填入恰当的单词。
注意:表格中的每个空格只填1个词 。
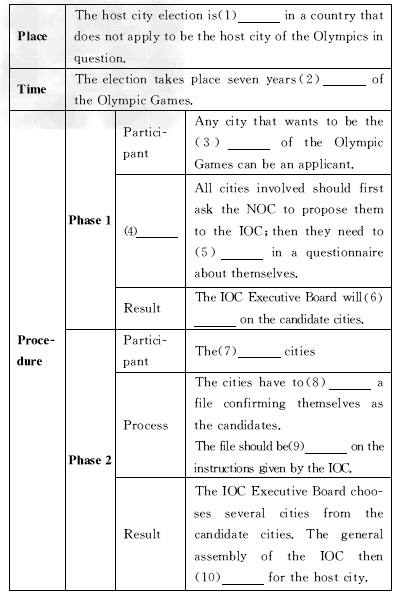
One of the roles of the International Olympic Committee(IOC)is to choose the host city for
the Olympic Games.The host city election takes place in a country which does not have a candidate
city for the Olympics in question.Except for unusual circumstances,the election is held seven years
before the Olympic Games take place.There have been two phases leading to the election of the
host city since December 1999.
Phase 1:applicant cities
Any city that wishes to host the Olympic Games must be proposed to the IOC by its National
Olympic Committee(NOC),with a letter from the city itself.During the first phase,which lasts around
ten months,each applicant city must answer a questionnaire to provide general information about itself.
Then the applications will be examined carefully.A number of things will be considered,such as
government support,public opinion,general infrastructure(基础设施),safety,accommodations and
transport.The IOC Executive Board(执行董事会)will determine which applicant cities will be accepted
as candidate cities.Only candidate cities can continue?with the procedure.
Phase 2:candidate cities
Candidate cities must provide a candidature file according to the instructions given by the IOC.After
all the files are examined and the IOC Evaluation Commission(评估委员会)produces its report,the
IOC Executive Board draws up a list of final candidate cities.The general assembly of the IOC then takes a vote on the host city.
Choosing the host city of the Olympics
1.held 2.ahead 3.host 4.Process 5.fill 6.decide/determine
7.candidate 8.provide 9.based 10.votes
