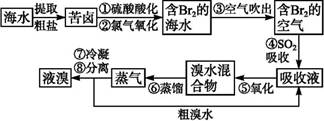
空气吹出法工艺,是目前“海水提溴”的最主要方法之一。其工艺流程如下:
(1)溴在周期表中位于 周期 族。
(2)步骤①中用硫酸酸化可提高Cl2的利用率,理由是
(3)步骤④利用了SO2的还原性,反应的离子方程式为
(4)步骤⑥的蒸馏过程中,温度应控制在80~90 ℃,温度过高或过低都不利于生产,请解释原因 。
(5)步骤⑧中溴蒸气冷凝后得到液溴与溴水的混合物,可利用它们的密度相差很大的特点进行分离。分离仪器的名称是 。
(6)步骤①、②之后并未直接用“含Br2的海水”进行蒸馏得到液溴,而是经过“空气吹出”“SO2吸收”“氧化”后再蒸馏,这样操作的意义是 。
(1)4 ⅦA
(2)酸化可抑制Cl2、Br2与水反应
(3)Br2+SO2+2H2O 4H++2Br-+S
4H++2Br-+S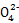
(4)温度过高,产生大量水蒸气,溴蒸气中水蒸气增加;温度过低,溴不能完全蒸出,吸收率低
(5)分液漏斗
(6)“空气吹出”“SO2吸收”“氧化”的过程实际上是Br2的浓缩过程,与直接蒸馏含Br2海水相比效率更高,耗能源少,使成本降低
(5)分离互不相溶的液体用分液方法;(6)海水中矿物质浓度太低,一般需要富集过程
