问题
选择题
有一个两端开口的玻璃管,用橡皮膜扎紧玻璃管的一端,灌满水后,用手堵住开口端,倒过来插入水槽中,如图所示,松手后,橡皮膜所呈现的是
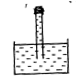
A.平面
B.凸起一些
C.凹进一些
D.无法判断
答案
答案:C
用橡皮膜扎紧玻璃管的一端,灌满水后,用手堵住开口端,倒过来插入水槽中时,橡皮膜上面的压强大于里面的压强,所以应该是凹进一些,选择C。
有一个两端开口的玻璃管,用橡皮膜扎紧玻璃管的一端,灌满水后,用手堵住开口端,倒过来插入水槽中,如图所示,松手后,橡皮膜所呈现的是

A.平面
B.凸起一些
C.凹进一些
D.无法判断
答案:C
用橡皮膜扎紧玻璃管的一端,灌满水后,用手堵住开口端,倒过来插入水槽中时,橡皮膜上面的压强大于里面的压强,所以应该是凹进一些,选择C。