人类历史发展为完整的世界史,经历了一个漫长而曲折的过程。这个过程包括两个方面:纵向发展和横向发展。其中纵向发展是指人类物质生产史上不同生产方式的演变和由此引起的不同社会形态的更迭,横向发展是指由彼此分散到逐步联系密切,终于发展为整体的过程。阅读材料,回答问题。
材料一 历史向世界历史的转变,不是“自我意识”、宇宙精神或者某个形而上学怪影的某种抽象行为,而是纯粹物质的、可能通过经验确定的事实,每一个过着实际生活的、需要吃、喝、穿的个人都可以证明这一事实。
——《马克思恩格斯全集》第三卷
材料二 图中的四幅图摘自斯塔夫里阿诺斯《全球通史》(图中白色部分是西方人眼中的世界)
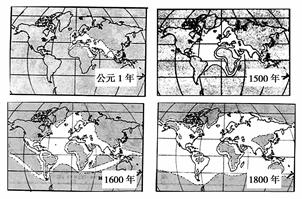
材料三 英国发生工业革命后……美洲、非洲、西亚、南亚、西南太平洋诸岛、大洋洲先后沦为殖民地……其他地区,包括很多欧洲国家,都不得不在西欧工业巨大优势的影响和压力下,先后不一地作出反应。
——吴于廑、齐世荣《世界史》
(1)根据材料一,概括人类历史向世界历史转变的动因。
(2)依据材料二中的四幅图,说说西方人眼中的世界发生了怎样的变化?试分析产生这一变化的主要原因。
(3)根据材料三及结合所学知识,概括工业革命后各地所作出的反应及影响。
(1)物质生产的发展(或生产力的发展)。
(2)变化:打破了相对分散、隔绝状态,了解范围逐渐扩大,地域性历史逐渐融合为世界历史。
原因:资本主义经济的发展;新航路的开辟;殖民扩张的加剧;新的交通工具及通讯手段的发明。
(3)反应:第一,通过改革或革命的手段扫除资本主义发展的障碍。
第二,实现工业化。
第三,殖民地半殖民地国家掀起民族解放运动。
第四,掀起社会主义运动。(写出两点即可)
影响:密切了国际交流;改变了世界格局,促进了世界殖民体系的形成;确立了资本主义世界市场,世界联系逐渐加强并成为一个整体。(写出两点即可)
(1)根据材料中“而是纯粹物质的、可能通过经验确定的事实,每一个过着实际生活的、需要吃、喝、穿的个人都可以证明这一事实。”可得答案。
(2)根据材料可知西方人中的世界范围在不断扩大且地区间的地理联系增强。通过所学知识可知,这种认识的变化具有多方面的原因,如新航路的开辟、通过殖民扩张、资本主义经济的发展和交通、通讯工具的革新促进对世界了解的加深。
(3)工业国家在殖民扩张和掠夺中传播了先进的思想及生产方式,其他国家和地区开始通过改革或革命的手段发展发展资本主义政治、经济制度,开启工业化生产;殖民地半殖民地国家在西方民族主义的影响下开始了民族解放运动。这些加强了世界各地之间的联系与交流,世界日益开始形成一个整体,世界殖民体系和资本主义世界市场形成并发展。
