问题
综合
结合图文材料,回答问题。
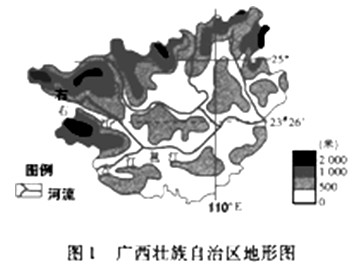
(1)图1中右江的流向为_________________,判断的依据是____________________________________。
(2)广西河流径流量的季节变化有何特点?请简述其原因。
___________________________________________________________________________________________
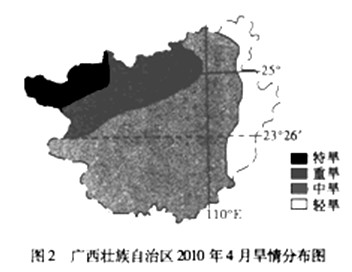
(3)据图2描述广西旱情的空间分布特点:__________________________________;请列举两项影响广西旱情分布的自然原因。
___________________________________________________________________________________________
答案
(1)自西北向东南;右江流域的地势自西北向东南降低。
(2)夏半年径流量大,冬半年径流量小(径流量季节变化大);夏半年降水量多,冬半年降水量少(降水量季节变化大)。
(3)旱情自西向东逐渐减轻;降水量东多西少(降水量分布不均);西部坡度大(西部地势高),地表水难以保存;西部地表土层较薄,难以保持水分;西部有石灰岩分布,易造成地表水渗漏。答出任意两项即可。