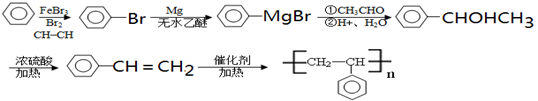
卤代烃(R-X)在醚类溶剂中与Mg反应可制得格氏试剂,格氏试剂在有机合成方面用途广泛。
已知: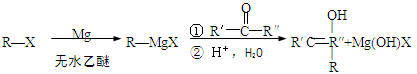
(R表示烃基,R′和R″表示烃基或氢)
某有机物A有如下转化:
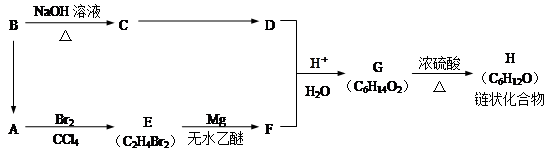
试回答下列问题:
(1)B→A的反应条件为__________________________,B→C的反应类型是_______________。
(2)G的结构简式是_______________________________。
(3)H中所含官能团的名称是________________________________________。
(4)写出一种满足下列条件的物质H的同分异构体的结构简式 ____________________________
①能发生银镜反应;②有三种不同氢原子;③含有最多的甲基
(5)聚苯乙烯(PS)由苯乙烯(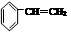 )聚合而成,是一种多功能塑料,广泛应用于食品包装,机器设备等许多日常生活领域中。写出以 D和苯为主要原料制备苯乙烯(
)聚合而成,是一种多功能塑料,广泛应用于食品包装,机器设备等许多日常生活领域中。写出以 D和苯为主要原料制备苯乙烯(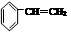 )的合成路线流程图,无机试剂任选。
)的合成路线流程图,无机试剂任选。
(合成路线常用表示方法为:A B ……
B …… 目标产物)
目标产物)
(1)NaOH醇溶液、△(1分) ;取代 (1分)
(2)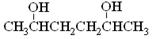 (2分)
(2分)
(3)碳碳双键、羟基 (2分)
(4)(CH3)3CCH2CHO (2分)
(5)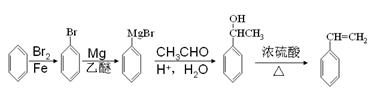 (4分)
(4分)
题目分析:A与单质溴反应生成B,则根据B的化学式可知A是乙烯,B是1,2-二氯乙烷,结构简式是CH2ClCH2Cl。B与Mg在无水乙醇的作用下反应,则根据已知信息可知,生成物F的结构简式是ClMgCH2CH2MgCl。B水解生成C,也能转化为乙烯,这说明B是一卤代乙烷,所以C是乙醇。乙醇含有羟基,转化为D,D能和F反应,则根据已知信息可知,D是乙醛,是乙醇氧化生成的。根据F和D的结构简式可知,G的结构简式是H3CCH(OH) CH2CH2CH(OH)CH3。G分子中含有2个羟基,在浓硫酸的作用下发生消去反应生成链状化合物I,则I的结构简式是H3CCH=CHCH2CH(OH)CH3。
(1)B→A是卤代烃的消去反应生成乙烯,则反应的化学反应方程式是CH3CH2Br+NaOH  NaBr+H2O+CH2=CH2↑。的反应条件为NaOH醇溶液、△,B→C的反应类型是卤代烃的水解反应,也是取代反应。
NaBr+H2O+CH2=CH2↑。的反应条件为NaOH醇溶液、△,B→C的反应类型是卤代烃的水解反应,也是取代反应。
(2)G的结构简式是H3CCH(OH) CH2CH2CH(OH)CH3。
(3)根据H的结构简式可知,H中所含官能团的名称是碳碳双键和羟基。
(4)①能发生银镜反应,说明含有醛基;②核磁共振氢谱有3个峰,说明含有3类等效氢原子;③拥有最多的甲基,所以根据H的结构简式可知,该同分异构体的结构简式是(CH3)3CCH2CHO。
(5)要制备聚苯乙烯,则可以通过逆推法完成。即首先制备苯乙烯,而碳碳双键的引入需要羟基的消去反应。要引入羟基则可以借助于已知信息,通过格林试剂与羰基的加成得到,因此正确的流程图是