问题
综合
根据材料和图,结合所学知识,回答下列问题。
云南苍山洱海地区山清水秀、林茂粮丰,大理古城宛如一颗明珠镶嵌在青山绿水之间,人与自然和谐统一。
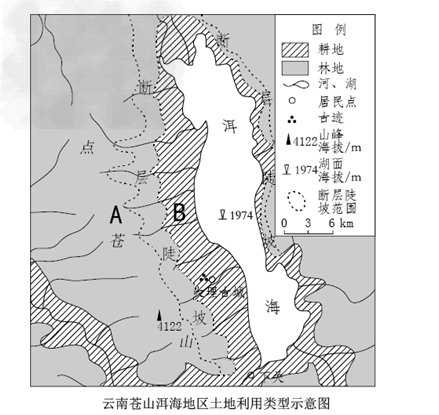
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________。
(2)如果在洱海西岸大规模建设住宅,可能对地理环境产生哪些不利影响?
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________。
答案
(1)断块山;洪积-冲积平原;内力作用形成断层,断裂面两侧岩体以垂直方向运动为主,A侧岩体相对上升,形成断块山;B侧岩体相对下降,形成谷地,同时流水等外力不断将风化、侵蚀产物搬运到谷地边缘堆积,形成洪积-冲积平原。
(2)占用耕地和湿地,影响农业生产,湿地的功能减弱、效益降低。人口增多,林地遭破坏,入湖污水增多,生物多样性减少,自然灾害增多,环境质量下降,不利于大理古城的保护,人地关系恶化。
