下表是某城市某日空气质量报告:

某研究性学习小组对表中首要污染物SO2导致酸雨的成因进行探究。(提示:SO2是一种无色、有刺激性气味的有毒气体,易溶于水,具有与CO2相似的化学性质)
【探究实验】实验一:用下图所示装置进行实验。
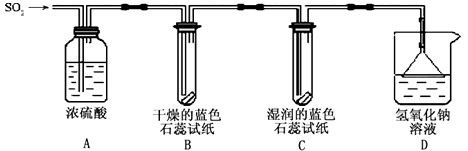
(1)A装置的作用是__________SO2气体。
(2)实验过程中,B装置内石蕊试纸的颜色没有发生变化,C装置内湿润的蓝色石蕊试纸变红色,说明SO2与水反应生成一种_________________。
(3)D装置的作用是__________,发生反应的化学方程式是______________。
实验二:往盛有水的烧杯中通入SO2气体,测所得溶液的pH______7(填“>”“=”或“<”),然后每隔1小时测定其pH,发现pH逐渐变小,直至恒定,说明烧杯中溶液被空气中的氧气氧化最终生成H2SO4。 【查阅资料】SO2形成酸雨的另一途径:SO2与空气中的O2在飘尘的作用下反应生成SO3(飘尘的质量和性质在反应前后不发生变化),SO3溶于降水生成H2SO4。在此过程中飘尘作______________。
【探究结论】SO2与空气中的氧气、水反应生成硫酸而形成酸雨。该市可能易出现酸雨。
【模拟实验】(1)由于食醋和酸雨的酸度(pH)差不多,因此酸雨对大理石的作用可以通过大理石碎片放在醋中来模拟。当把2.0g大理石碎片放在醋中一整夜后,取出固体干燥称重,其质量可能是(醋酸钙易溶于水)__________。A.小于2.0g B.正好2.0g C.大于2.0g
(2)这组学生还做了另一个实验,即将大理石碎片放在蒸馏水中过夜,其实验的目的是_____________。
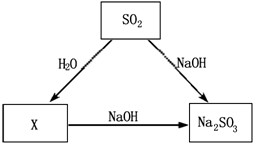
【知识联想】SO2具有与CO2相似的化学性质,根据下图给出的SO2及其化合物问的相互转化关系回答:X的化学式是_____,写出X与Na2SO3反应的化学方程___________________,反应类型是__________。
实验一:(1)干燥
(2)酸
(3)吸收SO2,防止污染空气SO2+2NaOH==Na2SO3+H2O
实验二:<;催化剂
(1)A
(2)与实验作对照,证明对大理石起腐蚀作用的是醋酸而不是水;
【知识联想】H2SO3;H2SO3+2NaOH==Na2SO3+2H2O;复分解反应(或中和反应)
