问题
计算题
(14分)如图,将质量m=1kg的圆环套在固定的倾斜直杆上,杆的倾角为37°,环的直径略大于杆的截面直径.对环施加一位于竖直平面内斜向上与杆夹角为37°的拉力F=10N,使圆环由静止开始沿杆加速度向上运动,已知环与杆间动摩擦因数μ=0.5.(g取10m/s2)求:
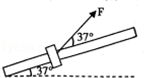
(1)F作用2s时圆环的速度是多大?
(2)2s后撤去力F,求圆环继续沿杆上滑的最大距离是多少?
答案
(1)2m/s;(2)0.2m;
题目分析:(1)以圆环为研究对象进行受力分析可得:
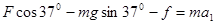 2分
2分
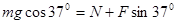 2分
2分
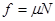 1分
1分
2s时圆环的速度: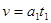 1分
1分
故解得: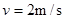 1分
1分
(2)撤去外力后,由牛顿第二定律及运动学公式可得:
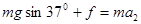 2分
2分
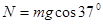 1分
1分
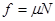 1分
1分
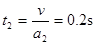 1分
1分
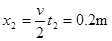 2分
2分
