如图为长颈鹿进化示意图,据图回答
:
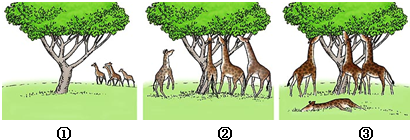
(1)图①说明古代长颈鹿祖先的个体之间颈长存在着______.
(2)图②说明地球环境变得干旱、缺乏青草时,______的个体容易生存下来.那么,长颈的变异就是______,短颈的变异是______.
(3)图③说明______个体能生存下来,并繁殖后代,______的个体被淘汰掉.
(4)从长颈鹿的进化过程看,颈长的变异是由于______改变而引起的.
(5)自然界中的生物,通过激烈的______,适应者生存下来,不适应者被淘汰,这就是______.
环境的定向选择--自然选择是进化生物学中最核心的概念,同时也是导致生物进化的关键因素.达尔文指出,自然界中各种生物普遍具有很强的繁殖能力,从而能产生大量的后代.而生物赖以生存的食物和空间都是非常有限的,任何生物要生存下去就得为获取足够的食物和空间而进行生存斗争即生存竞争.自然界中生物个体都有遗传和变异的特性,只有那些具有有利变异的个体,在生存斗争中才容易生存下去并繁殖后代,并将这些变异遗传给下一代,而具有不利变异的个体则容易被淘汰.自然界中的生物,通过激烈的生存斗争,适应者生存,不适应者被淘汰掉,这就是自然选择.古代的长颈鹿存在着颈长和颈短、前肢长和前肢短的变异,这些变异是可以遗传的,前肢和颈长的能够吃到高处的树叶,就容易生存下去,并且繁殖后代;前肢和颈短的个体,吃不到高处的树叶,当环境改变食物缺少时,就会因吃不到足够的树叶而导致营养不良,体质虚弱,本身活下来的可能性很小,留下后代的就会更小,经过许多代以后,前肢和颈短的长颈鹿就被淘汰了,这样,长颈鹿一代代的进化下去,就成了今天我们看到的长颈鹿.因此长颈鹿的长颈的形成就是长期自然选择的结果.
(1)生物界普遍存在着变异,古代的长颈鹿存在着颈长和颈短、前肢长和前肢短的变异,这些变异是可以遗传的.因此,图①说明古代长颈鹿祖先的个体之间颈长存在变异.
(2)变异是指子代与亲代之间的差异,子代个体之间的差异的现象.按照变异对生物是否有利分为有利变异和不利变异.有利变异对生物生存是有利的,不利变异对生物生存是不利的.图②说明地球环境变得干旱、缺乏青草时,长颈的个体能够吃到高处的树叶,就容易生存下去,并且繁殖后代;短颈的个体,吃不到高处的树叶.因此,长颈的变异就是有利变异,短颈的变异是不利变异.
(3)图③说明有利变异的个体能生存下来,并繁殖后代,不利变异的个体被淘汰掉.
(4)从长颈鹿的进化过程看,环境在决定长颈鹿变异个体的生存和淘汰进化过程中,起到了选择作用.
(5)自然界中的生物,通过激烈的生存竞争,适应者生存下来,不适应者被淘汰,这就是自然选择.
故答案为:(1)变异;
(2)长颈;有利变异;不利变异;
(3)有利变异;不利变异;
(4)环境;
(5)生存竞争;自然选择.
