(I)f(x)的定义域为(0,+∞),f′(x)=x-=
由f(x)在x=2处的切线与直线3x-2y+1=0平行,则f′(2)==,a=1….(4分)
此时f(x)=x2-lnx,f′(x)=
令f′(x)=0得x=1
f(x)与f′(x)的情况如下:
| x | (0,1) | 1 | (1,+∞) |
| f′(x) | - | 0 | + |
| f(x) | ↘ | | ↗ |
所以,f(x)的单调递减区间是(0,1),单调递增区间是(1,+∞)…(7分)
(II)由f′(x)=
由a>0及定义域为(0,+∞),令f′(x)=0得x=
①若≤1即0<a≤1在(1,e)上,f′(x)>0,
f(x)在[1,e]上单调递增,f(x)min=f(1)=;
②若1<<e,即1<a<e2在(1,)上,f′(x)<0,f(x)单调递减;在(,e)上,f′(x)>0,
f(x)单调递增,因此在[1,e]上,f(x)min=f()=a(1-lna);
③若≥e,即a≥e2在(1,e)上,f′(x)<0,
f(x)在[1,e]上单调递减,f(x)min=f(e)=e2-a
综上,当0<a≤1时,f(x)min=;当1<<e时,f(x)min=a(1-lna);当a≥e2时,f(x)min=e2-a…..(13分)

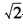 倍
倍