经测定乙醇的化学式是C2H6O,由于有机物普遍存在的同分异构现象,推测乙醇的结构可能是下列两种之一。
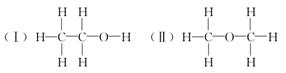
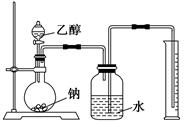
为测定其结构,应利用物质的特殊性进行定性、定量实验。现给出乙醇、钠、水及必要的仪器,请甲、乙、丙、丁四名同学直接利用如图给定装置进行实验确定乙醇的结构。
(1)学生甲得到一组实验数据:
| 乙醇的物质的量(mol) | 氢气的体积(L) |
| 0.10 | 1.12(标准状况) |
根据以上数据推断乙醇的结构应为________(用Ⅰ、Ⅱ表示),理由为_______________。
(2)同学乙分别准确称量4.60 g乙醇进行多次实验,结果发现以排到量筒内的水的体积作为生成的H2体积换算成标准状况后都小于1.12 L,如果忽略量筒本身及乙读数造成的误差,那么乙认为可能是由于样品中含有少量水造成的,你认为正确吗?________(填“正确”或“不正确”)如果你认为正确,请说明理由,如果你认为不正确,那产生这种情况的原因应该是什么?________________。
(3)同学丙认为实验成功的关键有:①装置气密性要良好
②实验开始前准确确定乙醇的量 ③钠足量 ④广口瓶内水必须充满 ⑤氢气体积的测算方法正确、数据准确。其中正确的有________。(填序号)
(4)同学丁不想通过称量乙醇的质量来确定乙醇的量,那么他还需知道的数据是_____________。
(5)实验后,四名同学从乙醇的可能结构分析入手对乙醇和钠的量的关系进行了讨论,如果乙醇的物质的量为n mol,那么对钠的物质的量的取值要求必须是_________________。
(1)Ⅰ 得出乙醇分子中有一个H与其他五个H不同,从而确定乙醇分子的结构为Ⅰ (2)不正确 广口瓶与量筒之间玻璃导管中水柱的体积没计算在内
(3)①②③⑤ (4)所给乙醇样品的密度 (5)大于n mol
(1)实验数据表明:1 mol C2H6O与足量的钠反应,产生标准状况下11.2 L H2,即0.5 mol H2,也就是1 mol H。说明1个C2H6O分子中只有1个氢原子被Na置换,故结构式为Ⅰ而不是Ⅱ。(2)乙同学认为样品中含少量水是错误的,因为2Na+2H2O=2NaOH+H2↑,且等质量的水产生的氢气比等质量的乙醇多,应大于1.12 L。H2体积小于1.12 L的原因是广口瓶与量筒之间玻璃导管中水柱的体积未计算在内。(3)同学丙关于实验成功的关键的五点中,只有④是不必要的,因为反应的烧瓶和导管中都存在空气,广口瓶中是否充满水并不影响实验的准确性。(4)同学丁不想称量乙醇的质量,则只有量取其体积,因此必须知道乙醇的密度。(5)本实验目的是推测乙醇分子的结构,乙醇必须作用完,若乙醇为n mol,由化学反应方程式知:2C2H5OH+2Na―→2C2H5ONa+H2↑,金属钠的物质的量必须大于n mol。
