(6分)海洋中蕴含丰富的资源。
(1)海水淡化是解决淡水不足的重要方法。下列净水方法中,可以使海水变为淡水的是 (填字母序号)。
A.过滤 B.吸附 C. 沉降 D. 蒸馏
(2)从海水中提炼出来的重水(D2O)可作原子能反应堆的中子减速剂和传热介质,重水中的重氢原子(D)核内有一个质子、一个中子。则重水中氧元素的质量分数为 。
(3)下图是采用膜分离技术的海水淡化装置,加压后,只有水分子可以通过淡化膜,其他 粒子不能通过淡化膜。加压前后,装置右侧海水中,下列各量减小的是 。
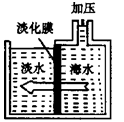
①溶质质量分数 ②溶剂质量 ③溶液质量 ④溶质质量
(4)从海水中制备食盐和金属镁的流程如下所示:
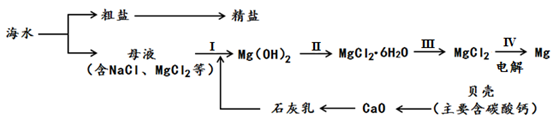
回答下列问题:
①步骤Ⅱ中需加入一种试剂并进行浓缩,所加试剂是 。
②粗盐中含有泥沙等杂质,用粗盐制取精盐的实验方法是 。
③上述流程中的反应不包含的基本反应类型是 。
(1)D (2)80% (3)②③
(4)①稀盐酸 ②溶解——过滤——蒸发 ③置换反应
题目分析:(1)A、过滤是除去不溶性杂质的方法,不能除去水中的可溶性物质,故错误;B、吸附是除去水中色素、异味等不溶性杂质的一种方法,不能除去水中的氯化钠、氯化镁等可溶性盐,故错误;C、沉降是使大颗粒不容物快速沉淀下来,不能除去水中的可溶性物质,故错误;D、蒸馏是通过加热的方法将水变成水蒸气,再冷凝成水的方法,可以得到最纯的蒸馏水,故可将水淡化,正确;(2)重水中的重氢原子的相对原子质量为2,则氧元素质量分数为: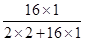 ×100%=80%;(3)海水中溶剂是水,由水分子可以透过淡化膜进入左侧淡水池,而海水中的各种离子不能透过淡化膜,说明加压后右侧海水中溶剂减少,溶质不变,所以溶液质量也减少,由于溶质不变,所以溶质质量分数增大,故②③正确;(4)①氢氧化镁为白色沉淀,与盐酸反应生成氯化镁;②粗盐中含有泥沙等杂质,用粗盐制取精盐的实验方法是溶解、过滤、蒸发;③把贝壳制成石灰乳,涉及反应:CaCO3 高温CaO+CO2↑、CaO+H2O═Ca(OH)2,分别属于分解反应、化合反应;在引入的海水中加入石灰乳,沉降、过滤、洗涤沉淀物,涉及反应:MgCl2+Ca(OH)2═Mg(OH)2↓+CaCl2,属于复分解反应;将沉淀物与盐酸反应,结晶、过滤、干燥产物,涉及反应:Mg(OH)2+2HCl=MgCl2+2H2O,MgCl2•6H2O△MgCl2+6H2O,分别属于复分解反应、分解反应;将产物电解得到金属镁,涉及反应:MgCl2通电Mg+Cl2↑,属于分解反应;没有涉及的反应为置换反应.
×100%=80%;(3)海水中溶剂是水,由水分子可以透过淡化膜进入左侧淡水池,而海水中的各种离子不能透过淡化膜,说明加压后右侧海水中溶剂减少,溶质不变,所以溶液质量也减少,由于溶质不变,所以溶质质量分数增大,故②③正确;(4)①氢氧化镁为白色沉淀,与盐酸反应生成氯化镁;②粗盐中含有泥沙等杂质,用粗盐制取精盐的实验方法是溶解、过滤、蒸发;③把贝壳制成石灰乳,涉及反应:CaCO3 高温CaO+CO2↑、CaO+H2O═Ca(OH)2,分别属于分解反应、化合反应;在引入的海水中加入石灰乳,沉降、过滤、洗涤沉淀物,涉及反应:MgCl2+Ca(OH)2═Mg(OH)2↓+CaCl2,属于复分解反应;将沉淀物与盐酸反应,结晶、过滤、干燥产物,涉及反应:Mg(OH)2+2HCl=MgCl2+2H2O,MgCl2•6H2O△MgCl2+6H2O,分别属于复分解反应、分解反应;将产物电解得到金属镁,涉及反应:MgCl2通电Mg+Cl2↑,属于分解反应;没有涉及的反应为置换反应.
