问题
问答题
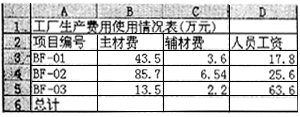
打开工作簿文件EX11.XLS(内容如下),将工作表sheet1的A1:D1单元格合并为一个单元格,内容居中;计算“总计”行的内容,将工作表命名为“生产费用表”。
答案
参考答案:
解析:打开工作表。合并单元格。在B6中键入“=SUM(B3:B5)”公式,双击此单元格,出现公式,向石拖动右下角的实心方块填充到其他需要产生结果的单元格。
打开工作簿文件EX11.XLS(内容如下),将工作表sheet1的A1:D1单元格合并为一个单元格,内容居中;计算“总计”行的内容,将工作表命名为“生产费用表”。

参考答案:
解析:打开工作表。合并单元格。在B6中键入“=SUM(B3:B5)”公式,双击此单元格,出现公式,向石拖动右下角的实心方块填充到其他需要产生结果的单元格。