问题
选择题
(10揭阳16).下列曲线不正确的是
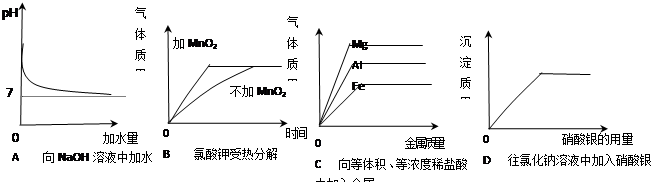
答案
答案:C
A、氢氧化钠溶液显碱性,加水时pH越来越小,但是不会小于7的.正确.
B、氯酸钾分解时,在二氧化锰的催化作用下反应速率加快,但是不会影响氧气的生成质量(本题对比的是催化剂的作用问题,所以在横坐标时间为零时气体不宜出现考虑就不是那么全面,其实C图也是如此,不是加入金属就会产生的气体的).正确.
C、足量的镁、铝、铁和稀盐酸反应时,生成氢气的多少取决于稀盐酸的量.当金属过量时,生成的氢气质量应该相等.不正确.
D、当氯化钠反应完后,沉淀的质量不再增加.正确.
故选C

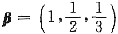 ,设A=αTβ,其中αT是α的转置,则An=______.
,设A=αTβ,其中αT是α的转置,则An=______.