根据如图实验装置图,按要求回答有关问题:
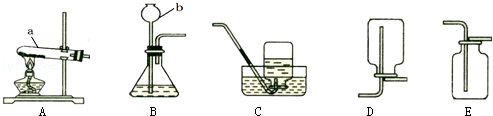
(1)写出图中带有标号仪器的名称:a ;b 。
(2)在实验室中用高锰酸钾制取氧气时,所发生的化学反应方程式为 。
(3)实验室制取二氧化碳气体,应选择的发生装置为 (填写装置的字母代号,下同);应选用的收集装置是 。检验二氧化碳是否收集满的方法是:将燃着的木条放在 ,观察火焰是否熄灭.二氧化碳溶于水的化学方程式为 。
(4)下列是初中化学部分重要的实验或实验装置。
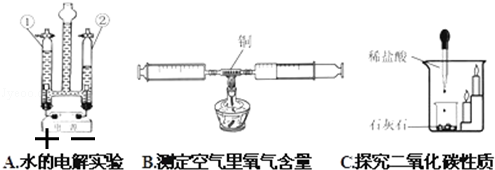
①A实验右边玻璃管②中产生的气体是 ;
②B实验如果实验数据小于21%,可能原因是 (写出一点);
③C实验蜡烛火焰熄灭说明二氧化碳具有的性质是 ;
(1)试管;长颈漏斗; (2)2KMnO4  K2MnO4 +MnO2 +O2↑;
K2MnO4 +MnO2 +O2↑;
(3)B; E;集气瓶口;CO2 +H2O=H2CO3 ;
(4))①氢气(或H2); ②装置漏气(或加热时间短,反应不充分;或铜的量太少,氧气没完全反应;或未冷却至室温就读数等);
题目分析:(1)标号仪器分别是试管和长颈漏斗;
(2)加热高锰酸钾生成锰酸钾、二氧化锰和氧气,方程式是:2KMnO4  K2MnO4 +MnO2 +O2↑;
K2MnO4 +MnO2 +O2↑;
(3)依据制取二氧化碳的反应物的状态、反应条件选择发生装置,依据二氧化碳的密度和溶解性选择收集装置,验满时应将燃着的木条放于集气瓶口,观察木条是否熄灭。实验室制取二氧化碳用大理石和稀盐酸常温反应,属于固液常温型,故选发生装置B;二氧化碳的密度比空气大且能溶于水,故最好用向上排空气法收集; 验满时应将燃着的木条放于集气瓶口,观察木条是否熄灭;二氧化碳溶于水的化学方程式为 CO2 +H2O=H2CO3;
(4)①依据电解水时生成的氢气与氧气的体积大小分析即可。电解水时生成的氢气与氧气的体积比是2:1,所以②中产生的气体是氢气;
②从测定空气中氧气的含量较实际值偏低的原因可能是:装置漏气或加热时间短,反应不充分;或铜的量太少,氧气没完全反应;或未冷却至室温就读数等;
③从二氧化碳能使火焰熄灭分析判断。石灰石可以与盐酸反应生成二氧化碳,蜡烛火焰熄灭说明二氧化碳不能燃烧,不支持燃烧。
